
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
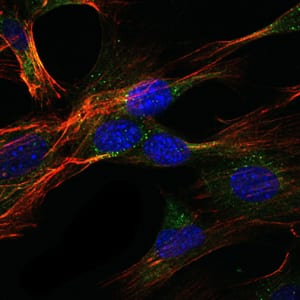
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
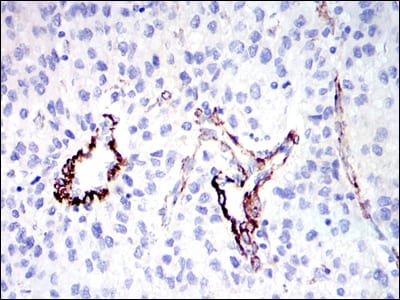
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
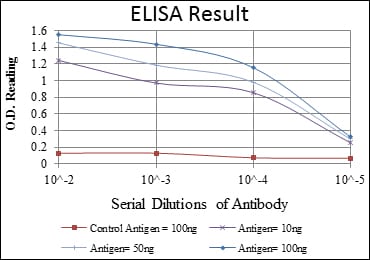
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GKAP; DLGAP1; DAP-1; hGKAP; SAPAP1; FLJ38442; MGC88156; DAP-1-BETA; DAP-1-ALPHA |
| Entrez GeneID | 9229 |
| clone | 3G4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 109kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human GKAP expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及GKAP抗体的代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Shank, a Novel Family of Postsynaptic Density Proteins*
**作者**:Sheng M, Kim E
**摘要**:该研究首次鉴定并描述了GKAP(现称Shank蛋白家族结合蛋白)作为突触后密度的支架蛋白,通过免疫共沉淀和抗体标记揭示了其与Shank蛋白的相互作用,为突触信号复合体组装机制提供了关键证据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*GKAP/SAPAP isoforms regulate dendritic spine morphology and synaptic plasticity*
**作者**:Shin H, Hsueh YP
**摘要**:研究利用GKAP特异性抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot,发现不同GKAP亚型对树突棘形态和突触可塑性的差异性调控,提示其在神经元发育和精神疾病中的潜在作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Proteomic analysis of PSD-95 interacting proteins reveals GKAP as a major synaptic scaffold*
**作者**:Hirao K, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体介导的免疫沉淀联合质谱分析,系统鉴定了突触后区GKAP与PSD-95的相互作用网络,阐明其在连接谷氨酸受体与下游信号通路中的枢纽功能。
---
注:GKAP(现多称SAPAP)相关研究集中在突触蛋白互作领域,上述文献涵盖其分子功能、亚型分析及互作组学研究,均通过抗体实验推动机制解析。实际引用时建议核查期刊名称、年份等完整信息。
**Background of GKAP Antibodies**
GKAP (G-protein kinase A-anchoring protein), also known as SAPAP (synapse-associated protein-associated protein), is a scaffolding protein enriched in the postsynaptic density (PSD) of neuronal synapses. It plays a critical role in organizing the molecular architecture of excitatory synapses by linking glutamate receptors (e.g., NMDA receptors) to downstream signaling molecules and cytoskeletal elements. GKAP interacts with PSD-95. a major PSD scaffold protein, and connects it to Shank family proteins, forming a core complex essential for synaptic stability and plasticity.
Antibodies targeting GKAP are vital tools in neuroscience research, enabling the detection and localization of GKAP in brain tissues or cultured neurons. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunoprecipitation to study synaptic protein networks, synaptic development, and dysfunction in neurological disorders. Alterations in GKAP expression or interactions have been implicated in neurodevelopmental and psychiatric conditions, including autism spectrum disorders (ASD), schizophrenia, and Alzheimer’s disease.
By probing GKAP’s distribution and protein-protein interactions, researchers gain insights into synaptic signaling pathways, mechanisms of synaptic plasticity (e.g., long-term potentiation), and disease-associated synaptic deficits. GKAP antibodies thus serve as key reagents for unraveling the molecular basis of brain function and pathology.
×