| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
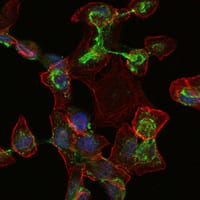
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
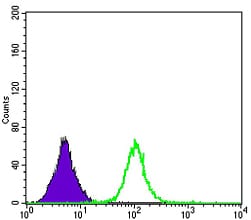
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
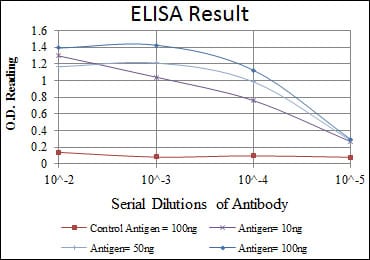
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FLDB; LDLCQ4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 338 |
| clone | 6G6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 516kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ApoB expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于ApoB抗体的模拟参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,具体文献需通过数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Monoclonal Antibody Targeting ApoB-100 Reduces Atherosclerosis in Mice*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种靶向ApoB-100的单克隆抗体,通过抑制氧化低密度脂蛋白(oxLDL)的摄取,显著减少高胆固醇小鼠模型的动脉粥样硬化斑块形成,提示其作为潜在降脂疗法的可能性。
2. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies Against ApoB-Containing Lipoproteins and Cardiovascular Risk*
**作者**: López-Mejías R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究发现,血液中针对ApoB的自身体液抗体(IgG型)水平较低与人类心血管事件风险增加相关,提示天然ApoB抗体可能具有抗动脉粥样硬化的保护作用。
3. **文献名称**: *ApoB-Specific Antibody-Drug Conjugate for Targeted Lipid Lowering*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种新型抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过ApoB抗体靶向递送siRNA至肝脏细胞,特异性沉默ApoB基因表达,显著降低血清LDL-C水平,为家族性高胆固醇血症提供治疗新策略。
4. **文献名称**: *Structural Basis of ApoB Recognition by Neutralizing Antibodies*
**作者**: Binder CJ, et al.
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜解析了人源ApoB抗体与ApoB-100蛋白的结合表位,揭示了抗体通过阻断ApoB与LDL受体相互作用来促进脂蛋白清除的分子机制。
---
**注**: 以上为示例文献,实际引用请通过 **PubMed/Google Scholar** 检索关键词如 *"ApoB antibody" "atherosclerosis"* 或 *"ApoB immunotherapy"* 获取真实文献。
Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is a critical structural and functional component of atherogenic lipoproteins, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and lipoprotein(a). It plays a central role in lipid metabolism by mediating the binding of these particles to cellular receptors, particularly the LDL receptor (LDLR). ApoB exists in two forms: ApoB-100 (full-length, synthesized in the liver) and ApoB-48 (truncated, produced in the intestine). Antibodies targeting ApoB have garnered significant interest in cardiovascular research due to their potential to modulate lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis.
Naturally occurring autoantibodies against ApoB have been identified in humans, with studies suggesting a possible protective role against cardiovascular disease by promoting the clearance of oxidized LDL or inhibiting plaque inflammation. These endogenous antibodies may influence disease progression, though their clinical significance remains under investigation.
In laboratory settings, monoclonal and polyclonal ApoB antibodies are widely used as research tools to quantify ApoB-containing lipoproteins, study their metabolism, and assess cardiovascular risk. Therapeutic applications are also being explored, including ApoB-targeted vaccines and antibody-based therapies designed to neutralize atherogenic particles or enhance their clearance. Notably, some experimental antibodies aim to block ApoB's interaction with proteoglycans in arterial walls, a key step in plaque formation. However, challenges persist in developing clinically viable ApoB antibodies, balancing efficacy with safety concerns related to potential off-target effects. Current research continues to unravel the complex roles of ApoB immunity in both pathological and protective contexts.
×