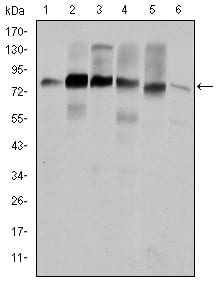
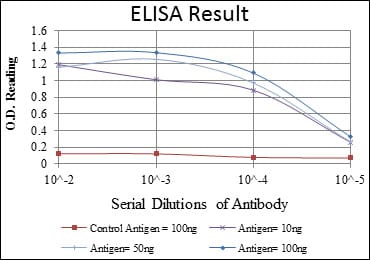
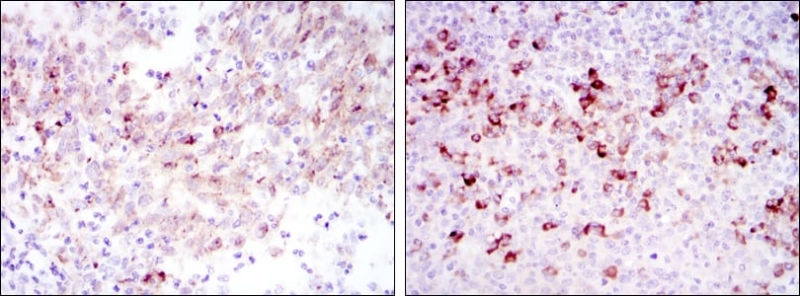
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EMS1; FLJ34459; CTTN |
| Entrez GeneID | 2017 |
| clone | 4C6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 80kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CTTN expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CTTN(Cortactin)抗体的代表性文献,按研究主题分类整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cortactin overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma*
**作者**:Yuan et al.
**摘要**:研究通过免疫组化(使用CTTN抗体)分析食管鳞癌组织中Cortactin蛋白表达水平,发现其高表达与肿瘤侵袭、淋巴结转移及患者生存率降低显著相关,提示其可作为预后标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Cortactin promotes cell motility by enhancing lamellipodial persistence*
**作者**:Weed et al.
**摘要**:利用Western blot和免疫荧光(CTTN抗体)证实Cortactin通过稳定肌动蛋白网络促进细胞伪足形成,从而增强肿瘤细胞迁移能力,机制涉及与Arp2/3复合物的相互作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Cortactin phosphorylation regulates invadopodia formation in breast cancer cells*
**作者**:Clark et al.
**摘要**:通过特异性CTTN抗体检测磷酸化修饰位点,发现EGFR信号通路激活的Cortactin磷酸化可促进乳腺癌细胞侵袭性伪足(invadopodia)的形成,为靶向治疗提供依据。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索最新研究,并关注抗体应用场景(如克隆号、实验方法及疾病模型)。
Cortactin (CTTN), encoded by the *CTTN* gene, is a multifunctional scaffolding protein involved in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics, cell adhesion, and membrane protrusion. It contains an N-terminal acidic domain, tandem cortactin repeats that bind F-actin, a proline-rich motif for interacting with SH3 domain-containing proteins, and a C-terminal SH3 domain. CTTN plays critical roles in cell migration, invasion, and vesicle trafficking by promoting actin polymerization and branching through interactions with the ARP2/3 complex. Overexpression or hyperactivation of CTTN is frequently observed in various cancers (e.g., breast, head and neck, colorectal), correlating with enhanced metastatic potential and poor prognosis.
CTTN-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation at Y421. S405/S418) in physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers use CTTN antibodies to explore its role in cancer progression, neuronal development, and immune cell functions. Commercial antibodies often target epitopes within the N-terminal region or cortactin repeats. Validation is critical, as CTTN shares homology with its neuronal paralog, cortactin-like (CTTNBP2). Dysregulated CTTN signaling has also been implicated in cardiovascular diseases and neurological disorders, broadening its research relevance.
×