| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
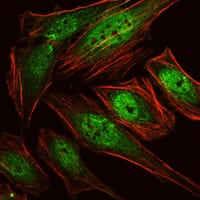
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
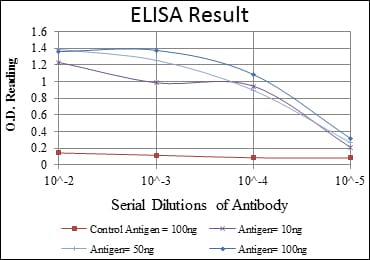
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AML1; CBFA2; EVI-1; AMLCR1; PEBP2aB; AML1-EVI-1; RUNX1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 861 |
| clone | 5A1 |
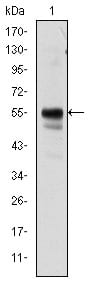
| WB Predicted band size | 55kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human RUNX1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RUNX1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"RUNX1 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis: Role in cellular differentiation and disease progression"*
**作者**:Ito Y et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨RUNX1在造血系统中的调控作用,利用特异性抗体检测RUNX1在白血病细胞中的异常表达,揭示其突变导致转录活性失调与急性髓系白血病(AML)的关联。
2. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-based detection of RUNX1 truncations in therapy-related myeloid neoplasms"*
**作者**:Osato M & Ito Y
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化方法,验证多种RUNX1抗体的特异性,发现截短型RUNX1蛋白在放化疗后继发性血液肿瘤中的高表达,提示其作为诊断标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*"ChIP-seq analysis of RUNX1 binding sites in hematopoietic progenitors using a novel monoclonal antibody"*
**作者**:Growney JD et al.
**摘要**:开发并验证一种高特异性抗RUNX1单克隆抗体,结合染色质免疫沉淀测序(ChIP-seq)技术,绘制造血干细胞中RUNX1的基因组结合图谱,揭示其在调控关键靶基因(如PU.1)中的功能。
4. **文献名称**:*"RUNX1 mutations impair hematopoietic differentiation by disrupting co-factor recruitment"*
**作者**:Sood R et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)结合RUNX1抗体,发现白血病相关突变会破坏RUNX1与CBFβ等辅因子的相互作用,导致造血分化阻滞及恶性转化机制。
这些研究均依赖不同RUNX1抗体的应用,涵盖疾病机制、诊断技术及基因组调控等领域。
**Background of RUNX1 Antibody**
The RUNX1 (Runt-related transcription factor 1) antibody is a critical tool for studying the RUNX1 protein, a member of the RUNX family of transcription factors that play pivotal roles in hematopoiesis, cellular differentiation, and oncogenesis. RUNX1. also known as AML1 (Acute Myeloid Leukemia 1), binds DNA via its conserved Runt domain and regulates gene expression by forming complexes with co-factors like CBFβ. It is essential for the development of hematopoietic stem cells and megakaryocyte maturation.
Dysregulation or mutations in RUNX1 are closely associated with hematologic malignancies, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Somatic mutations, chromosomal translocations (e.g., RUNX1-ETO in t(8;21) AML), or inherited RUNX1 variants can disrupt its normal function, leading to impaired differentiation and proliferation of blood cells.
RUNX1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression, localization, and interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). They also aid in diagnosing RUNX1-related disorders and evaluating therapeutic targets. Specific antibodies may recognize different isoforms (e.g., RUNX1a, b, c) or post-translational modifications, enabling precise investigation of its roles in health and disease. As RUNX1 continues to be a focus of cancer biology and stem cell research, its antibody remains indispensable for both basic and clinical studies.
×