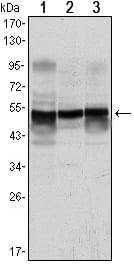
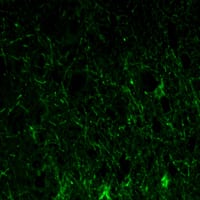
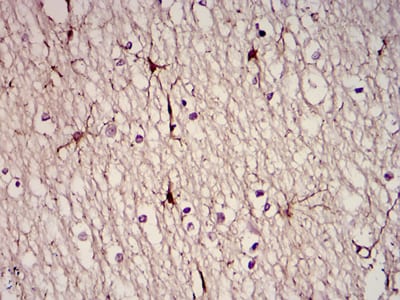
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FLJ45472; GFAP |
| Entrez GeneID | 2670 |
| clone | 6A6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human GFAP expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GFAP抗体的3-4篇参考文献(简要概括):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Isolation of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-specific antibodies: A review of GFAP structure, function, and its clinical implications in neuropathology"*
**作者**:Eng, L.F., et al.
**摘要**:该文献综述了GFAP蛋白的结构和功能,并探讨了针对GFAP的抗体在神经病理学中的应用,包括其在星形胶质细胞激活检测、脑肿瘤(如胶质瘤)诊断中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"GFAP antibodies in neurological disorders: Insights into astrocyte reactivity"*
**作者**:Pekny, M., & Pekna, M.
**摘要**:研究分析了GFAP抗体在阿尔茨海默病、多发性硬化等神经退行性疾病中的应用,强调GFAP作为星形胶质细胞激活标志物的动态变化及其与疾病进展的关联。
3. **文献名称**:*"Comparative analysis of GFAP antibody specificity across species and pathological conditions"*
**作者**:Middeldorp, J., & Hol, E.M.
**摘要**:通过比较不同GFAP抗体(如克隆GA5、6F2)的物种交叉反应性(人、小鼠、大鼠),评估其在神经炎症、创伤性脑损伤等模型中的检测灵敏度和特异性差异。
4. **文献名称**:*"GFAP isoforms and their roles in astrocyte heterogeneity: Implications for antibody-based studies"*
**作者**:Kamphuis, W., et al.
**摘要**:探讨GFAP的不同剪接变体(如GFAP-δ)在星形胶质细胞亚型中的表达差异,并指出选择特异性抗体对准确研究胶质瘢痕形成和神经再生的重要性。
---
这些文献覆盖了GFAP抗体的基础研究、疾病应用及技术优化方向,可作为相关领域的核心参考。
GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein) antibodies are immunological tools targeting GFAP, a key intermediate filament protein primarily expressed in astrocytes, the star-shaped glial cells of the central nervous system (CNS). Discovered in 1971. GFAP is critical for maintaining astrocyte structural integrity, modulating synaptic activity, and supporting the blood-brain barrier. Its expression is upregulated during astrocyte activation (astrogliosis), a hallmark of CNS injury, neurodegeneration (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis), infections, and autoimmune disorders like autoimmune GFAP astrocytopathy.
GFAP antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to identify astrocytes in tissue samples, assess neuroinflammatory conditions, and study glioma biology, as GFAP levels often correlate with tumor differentiation. In clinical settings, anti-GFAP autoantibodies in cerebrospinal fluid or serum aid in diagnosing autoimmune GFAP astrocytopathy, a treatable disorder presenting with meningoencephalitis, myelitis, or optic neuropathy.
Despite their specificity, GFAP isoforms and cross-reactivity with similar proteins in non-neural tissues (e.g., enteric glia) require careful validation. Recent advances in single-cell genomics have refined understanding of astrocyte diversity, prompting reevaluation of GFAP's role across subtypes. Overall, GFAP antibodies remain indispensable for exploring CNS pathophysiology and developing targeted therapies.
×