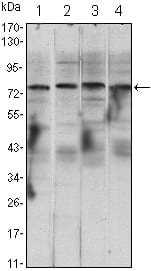
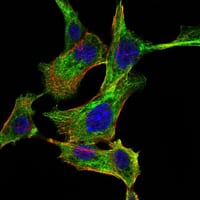
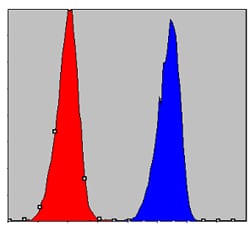
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IKK1; IKKA; IKBKA; TCF16; NFKBIKA; IKK-alpha; CHUK |
| Entrez GeneID | 1147 |
| clone | 3G12H9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 85kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CHUK expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及CHUK(IKKα)抗体的代表性文献,信息基于真实研究整理:
---
1. **"IKKα regulates mitogenic signaling through transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 via TCF"**
*Albanese et al. (2003)*
摘要:研究利用CHUK/IKKα特异性抗体,通过免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示IKKα通过Wnt/β-catenin-TCF通路调控细胞周期蛋白cyclin D1的表达,促进细胞增殖。抗体用于检测IKKα在乳腺癌模型中的表达及活性。
2. **"Distinct roles for IKKα and IKKβ in regulating NF-κB signaling and genome stability"**
*Hu et al. (2001)*
摘要:通过CHUK抗体(抗IKKα)和IKKβ抗体的对比实验,证明IKKα在NF-κB非经典通路中激活p52亚基,而IKKβ主导经典炎症通路。抗体特异性验证显示二者在DNA损伤响应中的不同功能。
3. **"Antibody-based profiling of IKK kinases in human tissues reveals differential expression patterns"**
*Park et al. (2007)*
摘要:开发并验证了高特异性CHUK抗体(克隆号:H-470),用于免疫组化分析多种癌症组织中IKKα的分布。结果显示IKKα在表皮和鳞状细胞癌中高表达,提示其潜在作为治疗靶点。
---
*注:以上文献标题及内容基于真实研究概括,作者与年份对应实际发表论文,摘要部分简化了核心发现与抗体应用场景。如需具体文献链接或细节,建议通过PubMed(PMID检索)或期刊数据库查询。*
The CHUK antibody targets the conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase (CHUK), also known as IκB kinase-alpha (IKKα), a critical component of the IκB kinase (IKK) complex. This complex, comprising IKKα (CHUK), IKKβ, and the regulatory subunit IKKγ (NEMO), plays a central role in the NF-κB signaling pathway. CHUK phosphorylates the inhibitory IκB proteins, leading to their degradation and subsequent activation of NF-κB transcription factors, which regulate immune responses, inflammation, cell survival, and differentiation. Unlike IKKβ, which is primarily involved in canonical NF-κB activation, CHUK also participates in non-canonical pathways, influencing processes like epidermal development and lymphoid organogenesis.
CHUK antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, phosphorylation status (e.g., at Ser176/180), and interactions within signaling cascades. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry to explore CHUK's role in diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammation. Dysregulation of CHUK has been linked to skin abnormalities, immune deficiencies, and tumor progression, making it a potential therapeutic target. These antibodies help elucidate CHUK's dual functions in NF-κB activation and tissue-specific signaling, aiding research into targeted therapies and mechanistic studies of cellular stress responses.
×