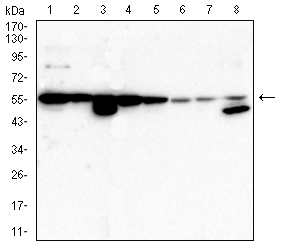
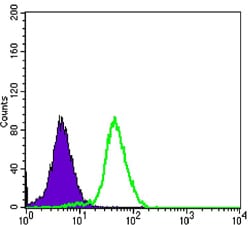
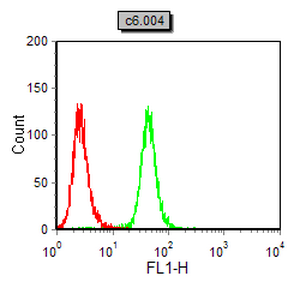
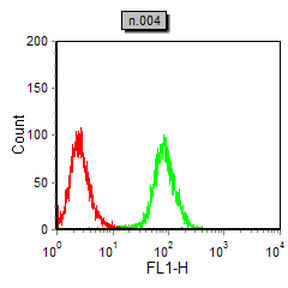
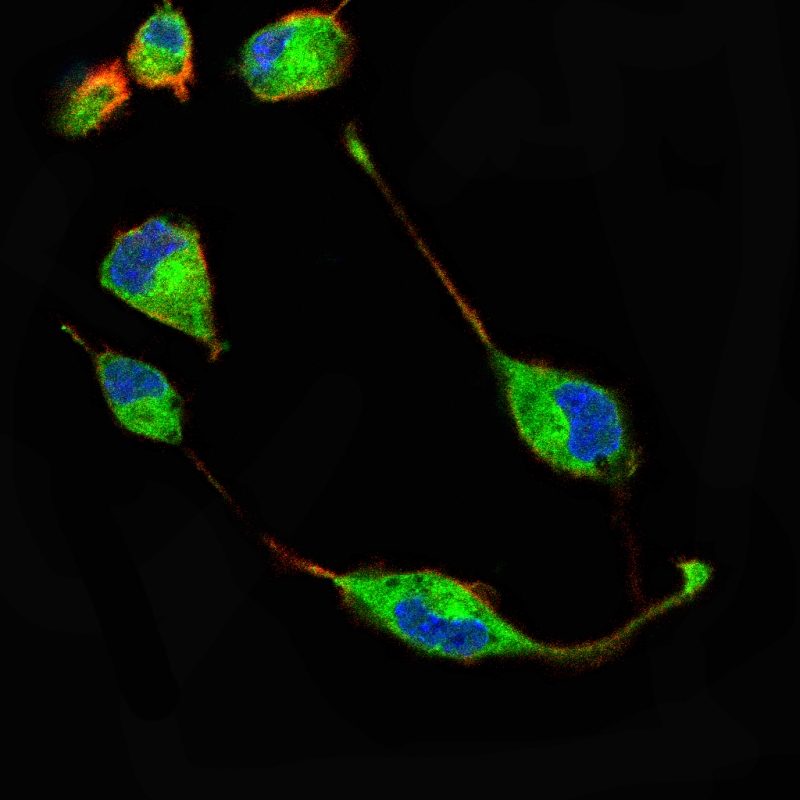
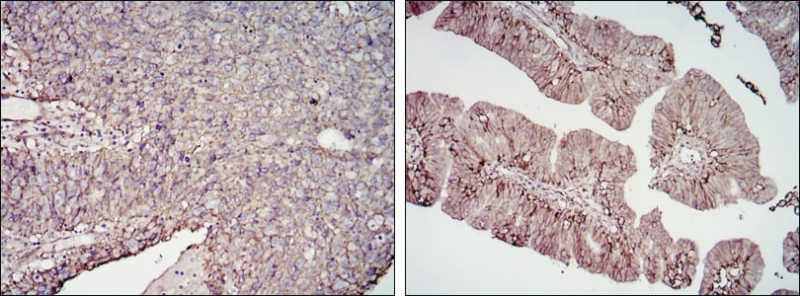
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7H3; B7-H3; 4Ig-B7-H3; CD276 |
| Entrez GeneID | 80381 |
| clone | 6A1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD276 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD276抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概述:
1. **文献名称**: *CD276 Antibody Enhances T Cell-Mediated Killing of Tumor Cells Through Immune Checkpoint Blockade*
**作者**: Zhou, Y., et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 该研究探讨了抗CD276抗体通过阻断免疫检查点增强T细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤作用。实验表明,CD276抗体可抑制肿瘤微环境中免疫抑制信号,并显著提升多种实体瘤模型中的抗肿瘤效果。
2. **文献名称**: *Structural Basis of CD276 Recognition by a Humanized Antibody for Cancer Immunotherapy*
**作者**: Zhang, L., et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜技术解析了人源化CD276抗体与抗原的结合表位,揭示了其高亲和力和特异性机制。研究为优化靶向CD276的抗体药物设计提供了结构基础。
3. **文献名称**: *CD276-Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugate Shows Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Solid Tumors*
**作者**: Seaman, S., et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 开发了一种CD276抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在多种实体瘤(如乳腺癌、肺癌)的临床前模型中表现出显著抑制肿瘤生长的效果,提示其作为新型治疗策略的潜力。
4. **文献名称**: *Dual Targeting of CD276 and PD-L1 with a Bispecific Antibody Improves Anti-Tumor Immunity*
**作者**: Lee, H., et al. (2022)
**摘要**: 研究设计了一种同时靶向CD276和PD-L1的双特异性抗体,在体内外实验中显示出协同增强T细胞活性和抑制肿瘤生长的双重作用,克服了单一靶向治疗的局限性。
以上文献涵盖了CD276抗体在免疫治疗机制、结构解析、药物开发及联合靶向策略中的应用。
CD276. also known as B7-H3. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 immune checkpoint family. Initially identified for its role in modulating T-cell responses, CD276 exhibits dual immune-regulatory functions, acting as both a co-stimulator and co-inhibitor in different contexts. Structurally, it contains immunoglobulin-like domains and is expressed on antigen-presenting cells, endothelial cells, and various tumor cells. In normal tissues, CD276 shows limited expression but is frequently overexpressed in multiple cancers, including lung, breast, and glioblastoma, where it correlates with poor prognosis, immune evasion, and metastasis.
CD276 antibodies are designed to target this protein, primarily for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. As a therapeutic tool, anti-CD276 antibodies aim to block its immune-suppressive activity, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Some are engineered as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) to deliver cytotoxic agents directly to CD276-expressing tumors. Preclinical studies highlight their potential in reducing tumor growth and improving survival. Additionally, CD276-targeting CAR-T cells and bispecific antibodies are under investigation.
Despite promise, challenges remain, including understanding CD276's pleiotropic signaling mechanisms, managing on-target/off-tumor effects due to low normal tissue expression, and addressing resistance pathways. Ongoing clinical trials (e.g., Phase I/II for solid tumors) continue to evaluate safety and efficacy, positioning CD276 as a compelling target in cancer immunotherapy.
×