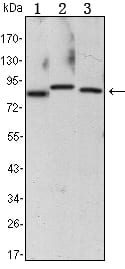
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IKK1; IKKA; IKBKA; TCF16; NFKBIKA; IKK-alpha; CHUK |
| Entrez GeneID | 1147 |
| clone | 3G12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 85kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CHUK expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CHUK(IKKα)抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其功能研究和应用方向:
---
1. **文献名称**:*IKK-1 and IKK-2: Cytokine-Activated IκB Kinases Essential for NF-κB Activation*
**作者**:DiDonato, J. A. et al.
**摘要**:该研究阐明了IKK复合物中IKKα(CHUK)和IKKβ的协同作用,证实两者在细胞因子诱导的NF-κB激活中不可或缺。通过特异性抗体检测,发现IKKα缺失会抑制特定炎症基因表达,为靶向IKK的炎症治疗提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*The IκB Kinase (IKK) Complex in NF-κB Regulation and Beyond*
**作者**:Häcker, H. & Karin, M.
**摘要**:文章系统综述了IKK复合物的结构、功能及调控机制,强调IKKα在非经典NF-κB通路和表皮分化中的作用。通过抗体实验揭示IKKα的亚细胞定位变化,提示其在发育和癌症中的双重角色。
3. **文献名称**:*Distinct Roles for IKKα and IKKβ in Inflammation and Skin Cancer*
**作者**:Hu, Y. et al.
**摘要**:利用基因敲除模型和特异性抗体,研究发现IKKα通过调控角质细胞分化抑制皮肤癌,而IKKβ主要介导炎症反应。抗体染色结果显示IKKα在肿瘤微环境中的表达异常,提示其作为癌症生物标志物的潜力。
---
以上文献涉及CHUK抗体的应用场景包括Western blot、免疫组化及功能机制研究,涵盖炎症、癌症等领域。如需具体实验细节,可进一步检索抗体货号或方法学论文。
**Background of CHUK Antibody**
The CHUK (conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase) antibody targets the CHUK protein, also known as IκB kinase alpha (IKKα), a critical component of the IKK complex within the NF-κB signaling pathway. CHUK/IKKα, along with IKKβ and NEMO (IKKγ), regulates the activation of NF-κB transcription factors by phosphorylating inhibitory IκB proteins, leading to their degradation and subsequent nuclear translocation of NF-κB. This pathway is pivotal in mediating immune responses, inflammation, cell survival, and proliferation.
CHUK antibodies are widely used in research to study the expression, localization, and function of IKKα in various biological contexts. They are essential tools in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to investigate CHUK's role in diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammation. For example, dysregulation of CHUK/IKKα has been linked to skin malignancies, rheumatoid arthritis, and aberrant immune activation.
These antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, with specificity validated through knockout controls or siRNA-based silencing. Researchers rely on CHUK antibodies to dissect signaling mechanisms, assess phosphorylation states, and explore therapeutic targets. Understanding CHUK's dual roles—canonical (NF-κB activation) and non-canonical (e.g., epidermal differentiation)—highlights its complexity, making specific antibodies crucial for unraveling its diverse cellular functions.
×