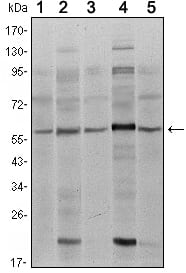
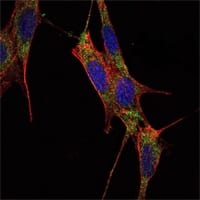
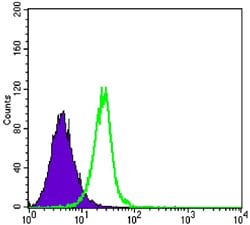
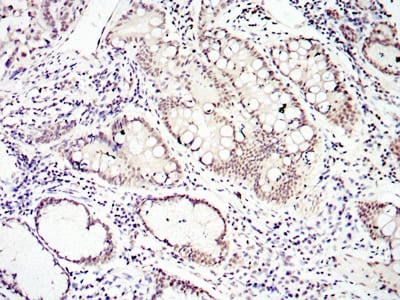
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | JIP; DPC4; MADH4; SMAD4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4089 |
| clone | 4G1C6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SMAD4 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SMAD4抗体的代表性文献(信息基于公开研究整理):
1. **文献名称**: *"SMAD4 Immunohistochemistry Reflects Genetic Status in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma"*
**作者**: Blackford A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究评估了多种SMAD4抗体在胰腺癌组织中的特异性,发现某些抗体(如EP618Y)能准确反映SMAD4基因缺失状态,可作为临床病理诊断的可靠标志物。
2. **文献名称**: *"Development and Validation of a Monoclonal Antibody Specific for SMAD4 in Colorectal Cancer"*
**作者**: Hua Z, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性小鼠抗人SMAD4单克隆抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot验证其在结直肠癌组织中的敏感性,并证明SMAD4蛋白表达缺失与患者预后不良相关。
3. **文献名称**: *"Comparative Analysis of SMAD4 Antibodies for Detection of TGF-β Signaling Defects"*
**作者**: Derynck R, et al.
**摘要**: 对比了兔多克隆抗体(如ab40759)和小鼠单克隆抗体在检测TGF-β通路中SMAD4蛋白表达的能力,发现不同抗体在福尔马林固定组织和冰冻切片中的性能差异,为实验选择提供指导。
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时请核对原文准确性并补充完整期刊、年份及卷页码。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“SMAD4 antibody validation”“SMAD4 immunohistochemistry”等关键词检索最新研究。
**Background of SMAD4 Antibody**
SMAD4. also known as DPC4 (Deleted in Pancreatic Carcinoma locus 4), is a critical tumor suppressor protein involved in the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway. This pathway regulates diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. SMAD4 acts as a central mediator by forming complexes with receptor-regulated SMADs (SMAD1. 2. 3. 5. 8/9) to translocate into the nucleus, where it modulates the transcription of target genes.
Mutations or deletions in the *SMAD4* gene are strongly associated with several cancers, notably pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, colorectal cancer, and juvenile polyposis syndrome. Loss of SMAD4 function disrupts TGF-β signaling, promoting tumor progression, metastasis, and resistance to therapies. Consequently, SMAD4 serves as both a biomarker for cancer prognosis and a potential therapeutic target.
SMAD4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in normal and diseased tissues. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP). Validated antibodies help detect SMAD4 levels in clinical samples, assess its nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling, and investigate interactions with other signaling molecules.
Researchers rely on SMAD4 antibodies to explore mechanisms underlying cancer development, fibrosis, and immune disorders. Specific clones (e.g., EP618Y) and antibody validation (e.g., knockout cell line controls) are critical to ensure accuracy, given the homology among SMAD family proteins and the potential for cross-reactivity. Overall, SMAD4 antibodies play a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of TGF-β signaling dysregulation in disease.
×