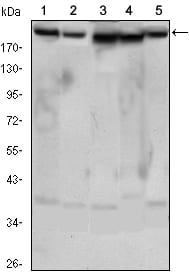
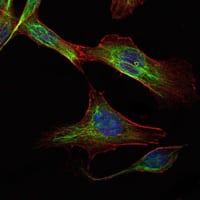
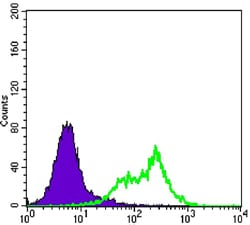
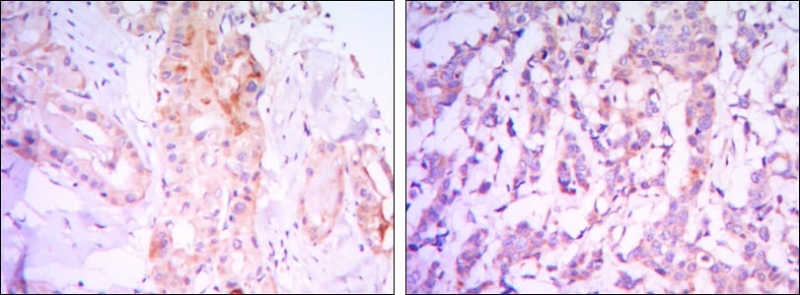
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Aliases | PIA; mAVO3; KIAA1999; MGC39830; DKFZp686B11164; RICTOR |
| Entrez GeneID | 253260 |
| clone | 7B3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 192kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human RICTOR expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RICTOR抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the Rictor-mTOR complex"
**作者**: Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM
**摘要**: 该研究首次鉴定了RICTOR作为mTORC2复合体的关键组分,并揭示了其在磷酸化Akt(Ser473)中的作用。研究中使用了特异性RICTOR抗体进行免疫沉淀,证实了mTORC2对细胞存活信号通路的调控。
2. **文献名称**: "RICTOR amplification promotes NSCLC cell migration through actin cytoskeleton remodeling"
**作者**: Masri J, et al.
**摘要**: 文章通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用RICTOR抗体)证明非小细胞肺癌中RICTOR基因扩增导致mTORC2活性增强,进而通过调节细胞骨架蛋白促进肿瘤细胞迁移和侵袭。
3. **文献名称**: "Characterization of RICTOR antibody specificity in mTORC2 function studies"
**作者**: Pearce LR, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究系统验证了多种商业化RICTOR抗体的特异性,发现部分抗体存在交叉反应性。通过基因敲除实验确认了可靠抗体在检测mTORC2复合体组装及下游信号分析中的关键作用。
*注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需核对原文。如需更近期研究,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar以“RICTOR antibody”及“mTORC2”为关键词检索。*
The RICTOR (Rapamycin-Insensitive Companion of mTOR) antibody is a crucial tool in studying the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2), a key regulator of cell growth, survival, and metabolism. RICTOR serves as a defining subunit of mTORC2. distinguishing it from mTORC1. Unlike mTORC1. mTORC2 is insensitive to rapamycin and phosphorylates substrates like AKT (at Ser473), SGK1. and PKCα, influencing processes such as cytoskeletal organization and apoptosis. Dysregulation of RICTOR/mTORC2 is linked to cancer, diabetes, and aging, driving interest in its therapeutic targeting.
RICTOR antibodies are widely used in biomedical research to detect protein expression, assess complex formation, and evaluate phosphorylation-dependent signaling. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunoprecipitation (IP), and immunofluorescence (IF). Specificity varies among commercial antibodies, requiring validation via knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated RICTOR depletion. Some antibodies target unique epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions) to avoid cross-reactivity with homologous proteins like Raptor (mTORC1 subunit).
Research applications include investigating mTORC2's role in tumor progression, metabolic disorders, and drug resistance. For example, RICTOR amplification in cancers correlates with poor prognosis, and its inhibition shows potential in preclinical models. However, challenges persist in distinguishing mTORC2-specific functions due to overlapping pathways and incomplete pharmacological inhibitors, underscoring the antibody's utility in mechanistic studies. Validated RICTOR antibodies remain essential for advancing mTOR-related therapeutic strategies.
×