| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
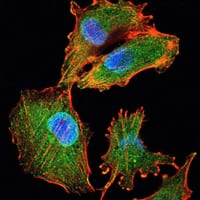
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
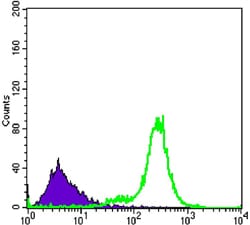
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL-34; C16orf77; MGC34647; IL34 |
| Entrez GeneID | 146433 |
| clone | 1D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human IL34 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于IL34抗体的3篇文献及其摘要的简要概括:
1. **"IL-34 promotes tumor progression by regulating tumor-associated macrophages in human cancers"**
- **作者**: Wei, S., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现IL34通过结合CSF1R调控肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)的存活和分化,促进肿瘤免疫抑制微环境。使用抗IL34抗体可阻断TAMs浸润,显著抑制小鼠肿瘤模型中的肿瘤生长和转移。
2. **"Targeting IL-34 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases: Insights from experimental models"**
- **作者**: Lin, H., et al.
- **摘要**: 在小鼠类风湿性关节炎模型中,IL34抗体通过抑制巨噬细胞介导的炎症反应,减轻关节破坏和疾病严重程度,提示其作为自身免疫疾病治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **"IL-34 neutralization ameliorates neuroinflammation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease"**
- **作者**: Ma, X., et al.
- **摘要**: IL34在小胶质细胞激活中起关键作用。抗IL34抗体治疗显著减少阿尔茨海默病模型中的神经炎症和淀粉样蛋白沉积,改善认知功能。
4. **"Development of a high-affinity anti-IL34 monoclonal antibody for diagnostic applications"**
- **作者**: Tanaka, R., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性抗IL34单克隆抗体,验证了其在ELISA和免疫组化中的应用,为IL34相关疾病的生物标志物检测提供了新工具。
以上研究覆盖了IL34抗体在治疗(肿瘤、自身免疫病、神经疾病)及诊断中的潜在应用。
Interleukin-34 (IL-34) is a cytokine discovered in 2008. known for binding to the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) and sharing functional overlap with macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1). IL-34 plays critical roles in regulating monocyte survival, differentiation, and tissue-specific macrophage homeostasis. It is implicated in various physiological and pathological processes, including neurodevelopment, inflammation, and immune regulation. Dysregulation of IL-34 has been linked to diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
IL-34 antibodies are tools developed to detect, neutralize, or modulate IL-34 activity in research and therapeutic contexts. Polyclonal and monoclonal IL-34 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to study IL-34 expression patterns in tissues or disease models. Neutralizing antibodies, in particular, help elucidate IL-34's role in CSF1R signaling and its crosstalk with pathways involved in tumor microenvironment modulation, osteoclastogenesis, and inflammatory responses. Recent studies explore IL-34 antibodies as potential therapeutics, targeting pathways involved in cancer progression (e.g., tumor-associated macrophage recruitment) or autoimmune diseases. However, challenges remain in optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Ongoing research aims to refine antibody engineering for clinical applications, including bispecific designs or combination therapies targeting IL-34/CSF1R axis components.
×