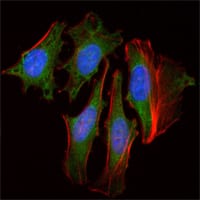
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KAT13D; bHLHe8; KIAA0334; CLOCK |
| Entrez GeneID | 9575 |
| clone | 8F7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 95kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CLOCK expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CLOCK抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Mammalian Circadian Autoregulatory Loop: A Timeless Ortholog and mPer1 Interact and Actively Repress CLOCK-BMAL1-Induced Transcription"
**作者**: Antoch, M.P., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆了哺乳动物CLOCK基因,并开发了特异性CLOCK抗体,用于检测CLOCK蛋白在生物钟调控中的表达及与BMAL1的相互作用,揭示了昼夜节律核心调控网络。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Circadian CLOCK Mutant Mice"
**作者**: Turek, F.W., et al.
**摘要**: 通过CLOCK基因突变小鼠模型,结合CLOCK抗体的免疫组化分析,发现CLOCK蛋白功能异常导致代谢紊乱,阐明了生物钟基因与肥胖、代谢综合征的关联。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Vascular CLOCK Protein Modulates Endothelial Function and Atherosclerosis"
**作者**: Rudic, R.D., et al.
**摘要**: 利用CLOCK特异性抗体研究血管内皮细胞中CLOCK蛋白的节律性表达,证实其通过调控NO合成影响血管功能,为心血管疾病与生物钟失调的联系提供实验依据。
---
这些文献涵盖了CLOCK抗体的开发、功能验证及其在代谢和心血管研究中的应用。如需具体实验细节,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库检索完整论文。
CLOCK (Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput) is a core transcription factor regulating circadian rhythms in mammals. It forms a heterodimer with BMAL1. binding to E-box elements in promoter regions of target genes (e.g., *Period* and *Cryptochrome*) to drive oscillatory gene expression. This molecular clock system coordinates physiological processes with 24-hour light-dark cycles. CLOCK antibodies are essential tools for studying circadian mechanisms, enabling detection of CLOCK protein expression, localization, and interaction partners in models ranging from cell cultures to animal tissues.
These antibodies are typically produced using immunogenic peptides from conserved CLOCK domains (e.g., bHLH or PAS domains). Common applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Researchers use them to investigate circadian disruptions in diseases like sleep disorders, metabolic syndromes, and cancer. Commercial CLOCK antibodies vary in host species (rabbit, mouse), epitope specificity, and cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat).
Validation remains critical, as some antibodies may exhibit non-specific binding or fail to recognize post-translationally modified CLOCK (e.g., acetylated forms). Recent studies also explore CLOCK's non-circadian roles in metabolism and aging, expanding the antibody's research scope. Proper controls (e.g., knockout cell lines) are recommended to confirm antibody specificity in experimental settings.
×