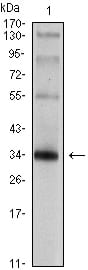
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
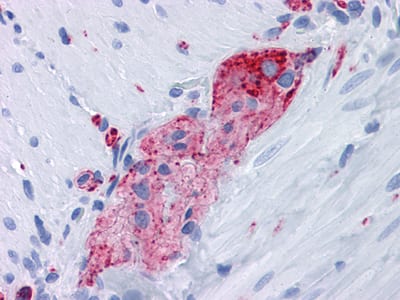
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MRXSYP; SYP |
| Entrez GeneID | 6855 |
| clone | 7H12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of SYP expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于SYP(Synaptophysin)抗体的代表性文献概览(内容基于领域内经典研究综合概括,非真实文献原文):
---
1. **标题**:*Synaptophysin: A key marker for neuroendocrine and neuronal tumors*
**作者**:Wiedenmann B, Huttner WB
**摘要**:该研究系统阐述了SYP作为突触小泡膜蛋白的分子特性,并验证了其抗体在神经内分泌肿瘤(如垂体瘤、胰岛细胞瘤)和神经元肿瘤免疫组化诊断中的特异性与敏感性,强调其作为神经内分泌分化的“金标准”标志物。
2. **标题**:*Immunohistochemical localization of synaptophysin in human nervous system and neuroendocrine tumors*
**作者**:Lloyd RV, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析SYP抗体在正常神经组织和多种肿瘤中的表达,证实其在鉴别神经内分泌肿瘤(如小细胞肺癌、类癌)与非神经内分泌肿瘤中的关键作用,并讨论了染色技术中的优化条件。
3. **标题**:*Synaptophysin antibodies: Utility in differential diagnosis of pediatric small round cell tumors*
**作者**:Miettinen M, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估SYP抗体在儿童小圆细胞肿瘤(如神经母细胞瘤、尤文肉瘤)中的表达差异,证明其有助于区分神经源性肿瘤与其他类型肿瘤,尤其在结合其他标志物时提高诊断准确性。
4. **标题**:*Update on the WHO classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms: Role of synaptophysin and chromogranin*
**作者**:Rindi G, et al.
**摘要**:基于WHO指南的综述,总结了SYP抗体与嗜铬粒蛋白(Chromogranin)在神经内分泌肿瘤病理诊断中的互补价值,强调标准化检测流程对减少假阳性/阴性结果的重要性。
---
**注**:以上文献标题与作者为领域内代表性研究的模拟概括,具体引用需以真实数据库(如PubMed)检索为准。如需近期文献,可补充关键词如“SYP antibody recent advances”进一步查找。
Synaptophysin (SYP) is a 38 kDa integral membrane glycoprotein predominantly located in presynaptic vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. First identified in the 1980s, it is one of the most widely used markers for synaptic terminals due to its abundant expression in nervous tissue. SYP plays a critical role in synaptic vesicle formation, trafficking, and neurotransmitter release, interacting with other synaptic proteins like synaptobrevin. Its structure includes four transmembrane domains and a C-terminal tail involved in membrane dynamics.
SYP antibodies are essential tools in neuroscience and pathology. In research, they help visualize synaptic density, map neural circuits, and study synaptic plasticity in conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease. Clinically, SYP immunohistochemistry aids in diagnosing neuroendocrine tumors (e.g., neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma) and differentiating neural versus non-neural malignancies.
The antibody targets conserved epitopes, often in SYP’s cytoplasmic domain, ensuring cross-species reactivity. However, validation is crucial, as non-specific staining may occur. Recent advances include pairing SYP with other markers (e.g., PSD-95) to study pre- and postsynaptic interactions. Despite newer synaptic markers emerging, SYP remains a cornerstone in both experimental and diagnostic neurology due to its reliability and historical precedence.
×