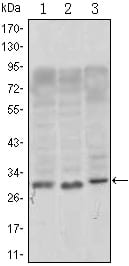
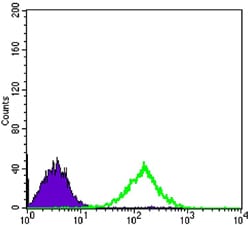
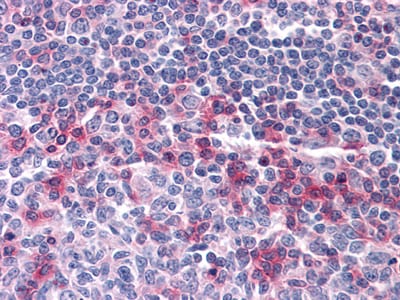
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CLEC2C; CD69 |
| Entrez GeneID | 969 |
| clone | 8B6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD69 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD69抗体相关的文献摘要概览:
1. **《CD69 is a stimulatory receptor for natural killer cell and its cytotoxic effect is blocked by CD69 antibody》**
- 作者:López-Cabrera, M. et al.
- 摘要:研究通过CD69抗体阻断实验,发现CD69在NK细胞活化中具有共刺激作用,抗体阻断显著抑制NK细胞的细胞毒性功能,表明CD69在天然免疫应答中的关键调控机制。
2. **《CD69 restricts the intensity of allergic contact dermatitis through limiting early T cell activation》**
- 作者:Sancho, D. et al.
- 摘要:利用CD69抗体检测小鼠模型,证明CD69通过负调控T细胞早期活化减轻接触性皮炎症状,揭示其作为免疫检查点分子的潜在治疗价值。
3. **《Anti-CD69 antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune uveitis》**
- 作者:Shi, G. et al.
- 摘要:开发人源化CD69单克隆抗体,在实验性葡萄膜炎模型中显示其通过抑制T细胞迁移和炎症因子释放,显著缓解眼部自身免疫反应,提示临床转化潜力。
4. **《CD69 mediates the interaction between neutrophils and macrophages during sepsis》**
- 作者:Liang, Y. et al.
- 摘要:使用CD69中和抗体证明,CD69通过介导中性粒细胞-巨噬细胞交互作用加剧脓毒症炎症风暴,阻断其信号通路可改善小鼠生存率。
CD69. a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the C-type lectin family, is an early activation marker expressed on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, NK cells, and macrophages. Discovered in the 1980s, it is encoded by the *CD69* gene in humans and plays a role in lymphocyte activation, adhesion, and inflammatory responses. CD69 forms homodimers and interacts with ligands such as S100A8/A9 proteins, triggering intracellular signaling pathways like MAPK and NF-κB to regulate immune cell functions.
CD69 antibodies are widely used as research tools to identify activated immune cells via flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry. They help study immune responses in infections, autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis), and cancer. In therapeutic contexts, CD69-targeting antibodies are explored for modulating immune activity—either suppressing aberrant immune activation in autoimmunity or enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Recent studies also highlight CD69's role in immune tolerance and its potential as a biomarker for disease progression or treatment response.
Ongoing research focuses on unraveling CD69's precise regulatory mechanisms and its interplay with other immune checkpoints, aiming to refine diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in immunology.
×