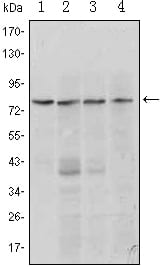
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BLIMP1; PRDI-BF1; MGC118922; MGC118923; MGC118924; MGC118925; PRDM1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 639 |
| clone | 5E7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 88kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PRDM1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于PRDM1抗体的参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Blimp-1 is required for the formation of immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and pre-plasma memory B cells*
**作者**:Shapiro-Shelef, M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用PRDM1(Blimp-1)抗体通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,揭示了Blimp-1在浆细胞分化和记忆B细胞形成中的关键作用,证明其缺失导致抗体分泌功能受损。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 regulates T cell homeostasis and function*
**作者**:Kallies, A., et al.
**摘要**:通过流式细胞术和免疫荧光染色(使用PRDM1抗体),研究显示Blimp-1在调节T细胞耗竭和维持外周T细胞稳态中起重要作用,为自身免疫疾病和癌症免疫治疗提供新视角。
---
3. **文献名称**:*PRDM1/Blimp-1: A regulator of plasma cell differentiation*
**作者**:Martins, G., & Calame, K.
**摘要**:综述总结了PRDM1在浆细胞分化中的核心调控机制,重点讨论了通过抗体染色和基因敲除实验揭示的PRDM1与其他转录因子(如PAX5)的相互作用网络。
---
4. **文献名称**:*PRDM1 suppresses colorectal cancer via modulation of IFN-γ response*
**作者**:Tamura, T., et al.
**摘要**:利用PRDM1抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现其在结直肠癌组织中表达下调,并通过调控干扰素-γ信号通路抑制肿瘤进展,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
以上文献均涉及PRDM1抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化、流式细胞术),涵盖免疫调控、癌症机制等领域。
PRDM1 (PR Domain Zinc Finger Protein 1), also known as BLIMP1 (B-Lymphocyte-Induced Maturation Protein 1), is a transcriptional repressor critical for terminal differentiation of immune cells. It belongs to the PRDM protein family characterized by an N-terminal PR (PRDI-BF1 and RIZ homology) domain and multiple zinc finger motifs. PRDM1 regulates cell fate decisions, particularly in B-cells, where it drives plasma cell differentiation by repressing genes associated with mature B-cell identity (e.g., PAX5. BCL6) and activating genes like XBP1. In T-cells, it suppresses effector functions and promotes regulatory T-cell development. Dysregulation of PRDM1 is linked to autoimmune diseases, lymphomas, and other malignancies.
PRDM1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles. These antibodies typically target specific epitopes within the PR domain or C-terminal regions. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to investigate PRDM1's involvement in immune regulation, cancer progression, and developmental biology. Commercially available PRDM1 antibodies vary in host species (e.g., mouse, rabbit) and clonality (monoclonal/polyclonal). Validation includes testing on PRDM1-deficient cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity. Researchers rely on these antibodies to explore PRDM1's dual role as a tumor suppressor (in B-cell malignancies) or oncogene (in certain T-cell cancers), as well as its therapeutic potential in modulating immune responses.
×