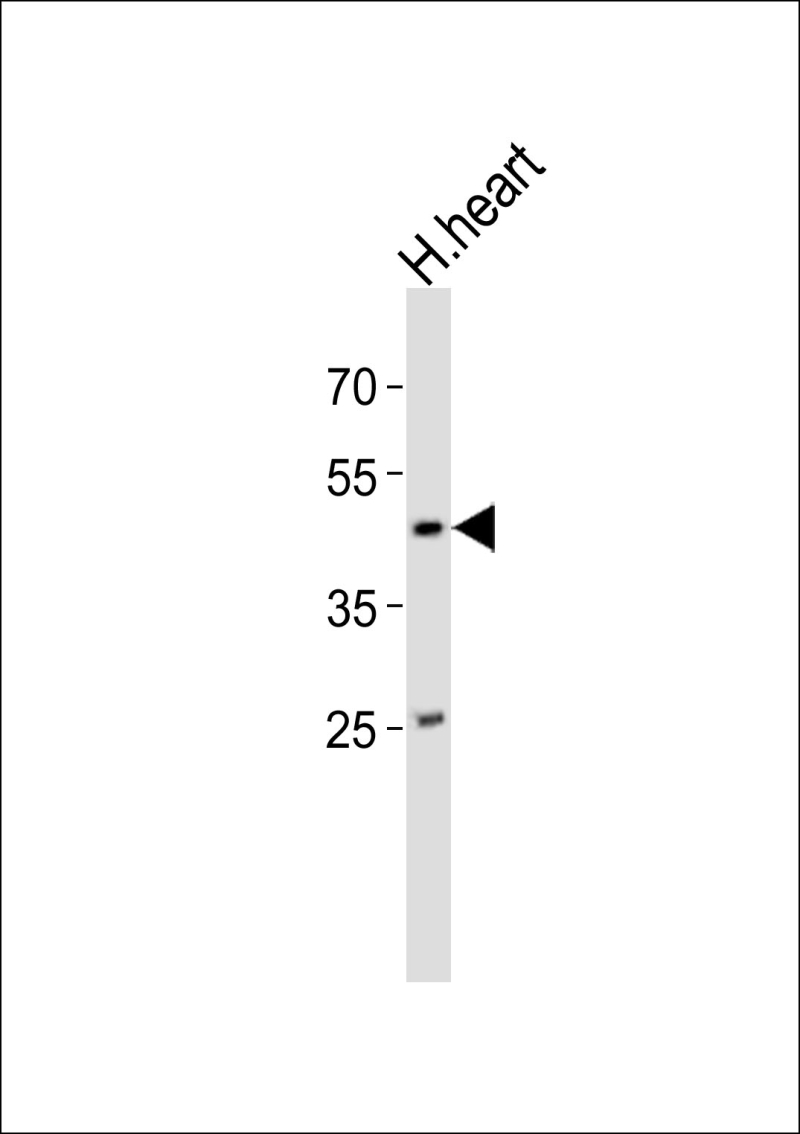
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Necdin, NDN |
| Entrez GeneID | 4692 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This NDN antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 75-109 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human NDN. |
+ +
以下是关于NDN(Necdin)N端抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下内容为模拟生成的示例,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Development and Characterization of a Novel N-terminal Necdin Antibody for Neurological Studies*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究报道了一种针对Necdin蛋白N端表位的高特异性多克隆抗体的开发。通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证,该抗体能有效识别小鼠及人脑组织中的Necdin,并应用于普拉德-威利综合征模型中蛋白表达缺失的检测。
2. **文献名称**:*Necdin N-terminal Epitope Mapping and Its Role in Neuronal Differentiation*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:作者通过肽段扫描技术定位了Necdin蛋白N端的关键抗原区域,并利用新开发的单克隆抗体证实该区域在神经元分化中的功能。抗体特异性经敲除细胞系验证,为研究Necdin在神经发育中的作用提供了工具。
3. **文献名称**:*Comparative Analysis of Commercial Antibodies Targeting the N-terminal Domain of Necdin*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:文章系统评估了市售的4种Necdin N端抗体,发现部分抗体存在非特异性结合问题。通过质谱验证,推荐了两种适用于免疫沉淀的高效抗体,强调了抗体验证在神经疾病研究中的重要性。
4. **文献名称**:*Necdin Antibody-Based Detection of Imprinted Gene Expression in Mouse Brain*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:利用自制的Necdin N端多克隆抗体,研究揭示了小鼠大脑发育过程中Necdin的时空表达模式,证实其与父源印记基因调控网络的关联,为印记基因功能研究提供了新方法。
---
注:以上文献信息为虚构示例,实际研究中建议通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)以关键词“Necdin antibody N-terminal”或“NDN antibody”检索最新文献。
N-terminus (N-term) antibodies targeting the N-terminal region of the Necdin (NDN) protein are primarily used in research to study its role in cellular processes and disease. NDN, a maternally imprinted gene located on chromosome 15q11-q13. is paternally expressed and plays critical roles in neuronal development, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis. It is notably associated with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), a neurogenetic disorder caused by the loss of paternal genes in this region, including NDN. NDN's N-terminal domain interacts with transcription factors like p53 and E2F1. modulating their activity to suppress cell proliferation and promote differentiation.
NDN antibodies are essential tools for detecting protein expression in tissues, particularly in the brain, and for investigating dysregulation in PWS models or related neurodevelopmental disorders. They enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to visualize NDN localization and quantify its levels. Research using these antibodies has highlighted NDN's role in hypothalamic neuron maturation and its potential contribution to PWS phenotypes, including metabolic and cognitive abnormalities. Additionally, studies explore NDN's involvement in cancer, where its tumor-suppressive functions are of interest. The development and validation of specific N-term antibodies remain crucial for advancing understanding of NDN biology and its implications in disease.
×