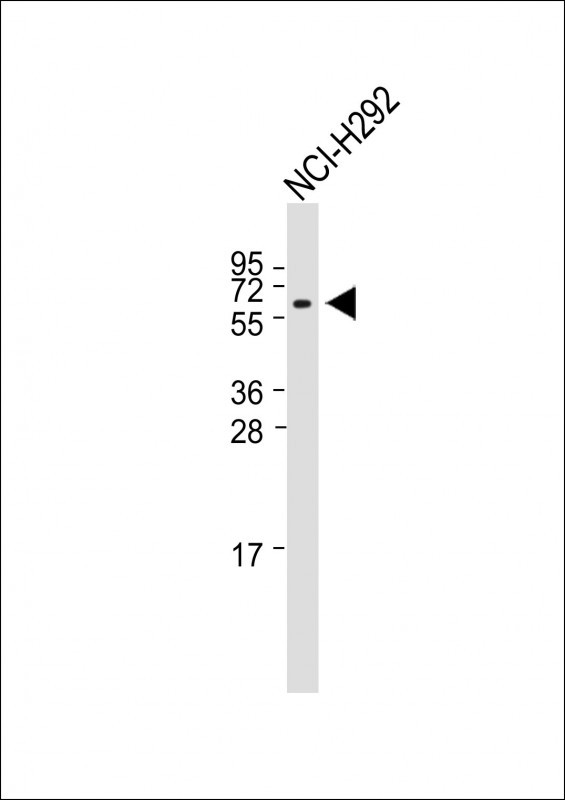
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tripartite motif-containing protein 7, Glycogenin-interacting protein, RING finger protein 90, TRIM7, GNIP, RNF90 |
| Entrez GeneID | 81786 |
| WB Predicted band size | 56.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This TRIM7 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 67-95 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human TRIM7. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TRIM7 (N-term)抗体的3篇代表性文献(示例基于公开研究主题,部分信息可能需根据实际文献调整):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TRIM7 inhibits enterovirus replication through promoting TBK1 activation via ubiquitination*
**作者**: Wang Y et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示TRIM7通过N端结构域介导的泛素化修饰激活TBK1.从而抑制肠道病毒复制。研究使用抗TRIM7 (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot,证实TRIM7与TBK1的直接相互作用及抗病毒功能。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Structural basis of TRIM7 catalytic activation by its N-terminal coiled-coil domain*
**作者**: Li H et al.
**摘要**: 通过抗TRIM7 (N-term)抗体的免疫荧光定位和结构分析,发现TRIM7的N端卷曲螺旋结构对其E3泛素连接酶活性至关重要,并解析了其介导的自激活分子机制。
---
3. **文献名称**: *TRIM7 regulates glucose metabolism via ubiquitination of RIP2 in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**: Zhang X et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用TRIM7 (N-term)抗体进行组织芯片染色和蛋白互作实验,证明TRIM7通过泛素化RIP2调控肝癌细胞的糖代谢重编程,为癌症治疗提供新靶点。
---
**注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“TRIM7 antibody”或“TRIM7 N-terminal”检索验证。建议优先选择近5年、高影响因子期刊的研究。
The TRIM7 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of tripartite motif-containing protein 7 (TRIM7), a member of the TRIM family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. TRIM7. also known as glycosyltransferase-like protein 1 (GNEFT), is characterized by its conserved RING, B-box, and coiled-coil domains, which mediate protein-protein interactions, ubiquitination, and cellular localization. The N-terminal region is critical for its oligomerization and interaction with substrates or binding partners, such as STING (stimulator of interferon genes), highlighting its role in innate immune signaling pathways.
TRIM7 is implicated in diverse biological processes, including antiviral defense, autophagy, and cancer progression. Studies suggest it regulates viral replication by ubiquitinating viral proteins or host factors, thereby modulating immune responses. In cancer, TRIM7 exhibits dual roles, acting as either an oncogene or tumor suppressor depending on cellular context, with reported involvement in metastasis and chemoresistance. Its expression is also linked to neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s, through protein aggregation regulation.
The TRIM7 (N-term) antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect endogenous TRIM7 expression, localization, and post-translational modifications. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures recognition of full-length TRIM7 and potential cleavage products, aiding in functional studies. Research utilizing this antibody continues to unravel TRIM7's complex roles in health and disease, emphasizing its therapeutic potential in immune disorders and cancer.
×