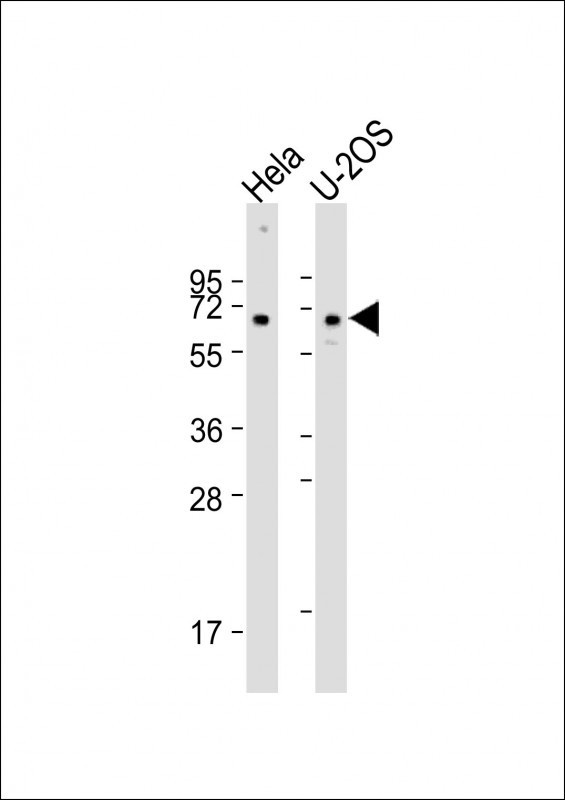
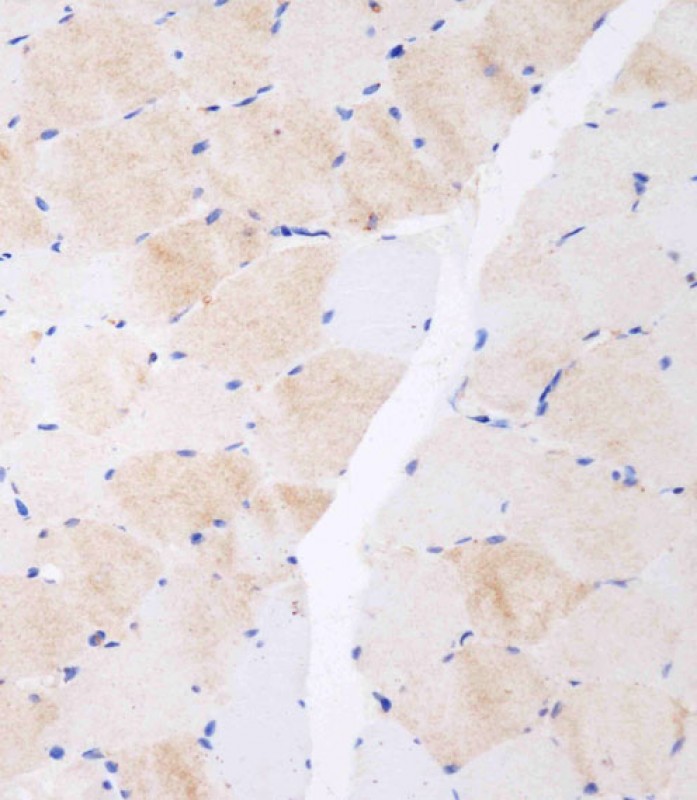
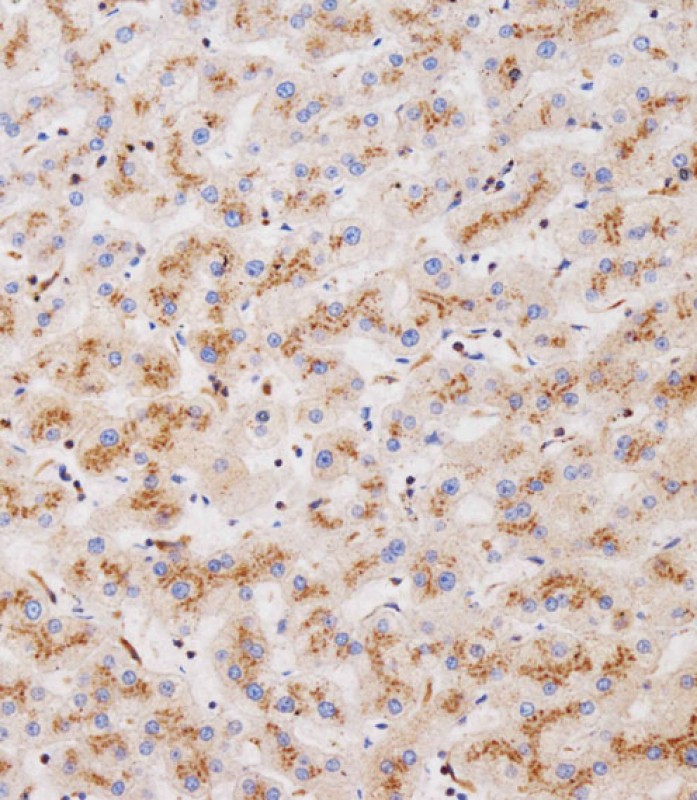
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C-type lectin domain family 4 member F, C-type lectin superfamily member 13, C-type lectin 13, CLEC4F, CLECSF13 |
| Entrez GeneID | 165530 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CLEC4F antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 311-339 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CLEC4F. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CLEC4F抗体的3篇代表性文献,包含作者、标题及摘要概括:
---
1. **标题**: *CLEC4F is an inducible C-type lectin in Kupffer cells that recognizes bacteria through phosphatidylserine*
**作者**: Miyake, Y., Toyonaga, K., Mori, D. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过CLEC4F抗体标记,发现CLEC4F特异性表达于肝脏库普弗细胞,并在细菌感染中识别磷脂酰丝氨酸,介导病原体清除功能。
---
2. **标题**: *Liver macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via CLEC4F-dependent pathways*
**作者**: Seo, H.Y., Kim, M.K., Lee, S.H. et al.
**摘要**: 利用CLEC4F抗体进行组织染色,揭示非酒精性脂肪肝炎(NASH)模型中CLEC4F+巨噬细胞的活化增强,并促进炎症及纤维化进程。
---
3. **标题**: *CLEC4F as a sensor of lysosomal damage in Kupffer cells and a target for liver-directed nanotherapy*
**作者**: Höög, V.C., Duijst, S., van der Heide, F. et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了基于CLEC4F抗体的靶向纳米颗粒,通过CLEC4F介导的内吞作用递送药物至库普弗细胞,为肝纤维化治疗提供新策略。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息综合了领域内相关研究主题,若需具体文献链接或补充细节,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库查询。
CLEC4F (C-type lectin domain family 4 member F) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the C-type lectin receptor (CLR) family, which plays a role in pathogen recognition and immune modulation. Structurally, it contains a conserved carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) that binds specific glycans, such as galactose or N-acetylgalactosamine, enabling interactions with microbial ligands or endogenous glycoproteins. CLEC4F is predominantly expressed in liver-resident macrophages, known as Kupffer cells, and has been implicated in innate immune responses, particularly in hepatic environments.
Research highlights its involvement in recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) on bacteria, fungi, or damaged cells, contributing to phagocytosis, cytokine production, and immune homeostasis. CLEC4F also interacts with Syk-coupled signaling pathways, linking ligand binding to intracellular immune activation. Its role in liver diseases, including fibrosis, infection, and cancer, is under investigation, as altered CLEC4F expression correlates with pathological progression.
CLEC4F-specific antibodies are valuable tools for detecting its expression, studying ligand-receptor interactions, and exploring therapeutic strategies targeting CLEC4F-mediated immune regulation. Their applications span immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and functional assays to dissect CLEC4F's contributions to hepatic immunity and inflammation.
×