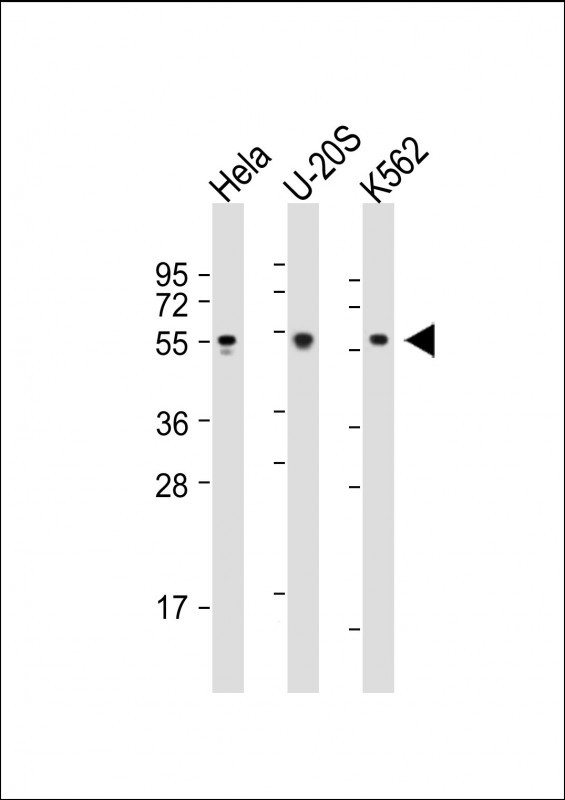
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Autoimmune regulator, Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy protein, APECED protein, AIRE, APECED |
| Entrez GeneID | 326 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This AIRE antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 64-92 amino acids from the Central region of human AIRE. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3条关于AIRE抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against type I interferons in AIRE deficiency*
**作者**:Meager A. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,AIRE基因缺陷导致的自身免疫性多内分泌腺病综合征I型(APS-1)患者体内存在高滴度的抗干扰素-α和干扰素-ω的自身抗体,这些抗体可能直接参与疾病发生,并可作为诊断标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**:*AIRE mutations and autoantibody profiles in patients with APS-1*
**作者**:Söderbergh A. et al.
**摘要**:通过分析APS-1患者的AIRE基因突变谱,发现患者血清中普遍存在针对AIRE蛋白的自身抗体,且抗体水平与疾病严重程度相关,提示其在自身免疫病理中的潜在作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*The diagnostic value of AIRE antibody detection in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy*
**作者**:Kisand K. et al.
**摘要**:研究表明,检测AIRE抗体(尤其是针对其PHD锌指结构域的抗体)可作为APS-1的早期诊断工具,其敏感性和特异性优于传统临床标准,有助于区分其他自身免疫疾病。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Thymic AIRE regulates the balance between immune tolerance and autoimmunity*
**作者**:Yamano T. et al.
**摘要**:在小鼠模型中证实,AIRE蛋白缺失导致胸腺中自身抗原表达异常,进而引发针对AIRE的自身抗体产生,破坏T细胞中枢耐受,最终诱发多器官自身免疫反应。
---
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对具体来源及内容准确性。)
AIRE (Autoimmune Regulator) antibodies are autoantibodies targeting the AIRE protein, a transcription factor crucial for immune tolerance. The AIRE gene, primarily expressed in thymic medullary epithelial cells (mTECs), promotes the expression of tissue-specific antigens (TSAs) during T-cell development. This process enables the deletion of self-reactive T cells, preventing autoimmune responses. Mutations in AIRE cause autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1/APECED), characterized by multi-organ autoimmunity and chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis.
In APS-1 patients, AIRE dysfunction leads to impaired thymic T-cell selection and the emergence of autoreactive T cells. Consequently, autoantibodies against AIRE itself or other organ-specific antigens (e.g., adrenal, pancreatic, or thyroid proteins) are frequently detected. Anti-AIRE antibodies are rare but serve as biomarkers for APS-1 diagnosis, complementing genetic testing. They may also arise in thymoma or other autoimmune conditions, reflecting AIRE dysregulation.
Research on AIRE antibodies aids in understanding autoimmune pathogenesis and tolerance mechanisms. Their detection involves immunoassays like ELISA or indirect immunofluorescence. However, their clinical utility beyond APS-1 remains limited, necessitating further studies to explore their role in broader autoimmune contexts. AIRE’s interplay with immune regulation continues to inform therapeutic strategies for autoimmune diseases.
×