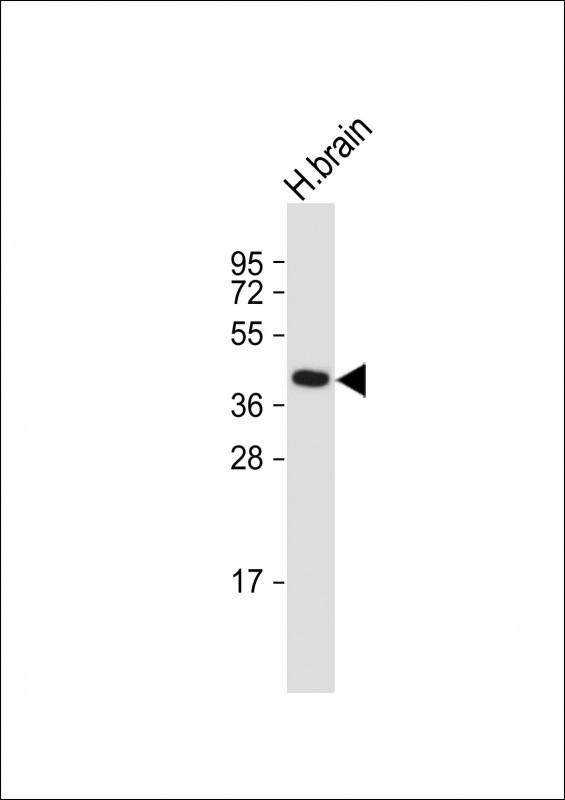
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GDNF family receptor alpha-like, GFRAL, C6orf144 |
| Entrez GeneID | 389400 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GFRAL antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 366-394 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human GFRAL. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GFRAL抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要概括如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*GFRAL is a receptor for the anorexigenic and anti-obesity cytokine GDF15*
**作者**:Yang et al. (2017)
**摘要**:该研究首次确定GFRAL是GDF15的受体,并证明其在脑干中特异性表达。通过使用抗GFRAL抗体阻断信号,发现小鼠的GDF15诱导的食欲抑制和体重减轻效应被逆转,提示GFRAL抗体在代谢调控中的潜在治疗价值。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The metabolic effects of GDF15 are mediated by the orphan receptor GFRAL*
**作者**:Emmerson et al. (2017)
**摘要**:研究通过体内实验证实,抗GFRAL抗体可阻断GDF15对高脂饮食诱导肥胖小鼠的代谢改善作用,包括抑制体重增长和改善葡萄糖耐受性,表明GFRAL抗体在干预肥胖相关代谢疾病中的作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*GFRAL Neutralization Antibodies Enhance Food Intake and Body Weight in Obese Mice*
**作者**:Mullican et al. (2018)
**摘要**:通过开发特异性中和性GFRAL抗体,研究证明阻断GFRAL/GDF15信号通路可显著增加肥胖模型小鼠的摄食量和体重,为靶向该通路的抗体在代谢综合征中的双向调节提供了依据。
---
如需具体论文链接或补充信息,可进一步提供DOI或PubMed ID。
GFRAL (Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Family Receptor Alpha-Like) is a transmembrane receptor identified in 2017 as the high-affinity receptor for Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15), a cytokine involved in metabolic regulation. GFRAL is primarily expressed in the hindbrain regions, notably the area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarius, which are critical for energy homeostasis and nausea responses. Its interaction with GDF15 has been linked to appetite suppression, weight loss, and glucose metabolism modulation, positioning the GFRAL-GDF15 axis as a key player in metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, and cancer-associated cachexia.
Antibodies targeting GFRAL have emerged as potential therapeutics to modulate this pathway. Neutralizing GFRAL antibodies, for instance, aim to block GDF15 binding, potentially counteracting its anorexic effects in conditions like cancer cachexia. Conversely, agonist antibodies might mimic GDF15 signaling to treat obesity by promoting satiety. Preclinical studies in animal models demonstrate that GFRAL antibody interventions can alter body weight and metabolic parameters, though efficacy and safety profiles vary depending on the antibody’s mechanism (antagonist vs. agonist).
Challenges remain, including understanding tissue-specific signaling nuances and mitigating off-target effects. Despite this, GFRAL antibodies represent a promising avenue for addressing metabolic diseases, with several candidates advancing to early-stage clinical trials. Their development underscores the growing interest in targeting neuro-metabolic pathways for therapeutic benefit.
×