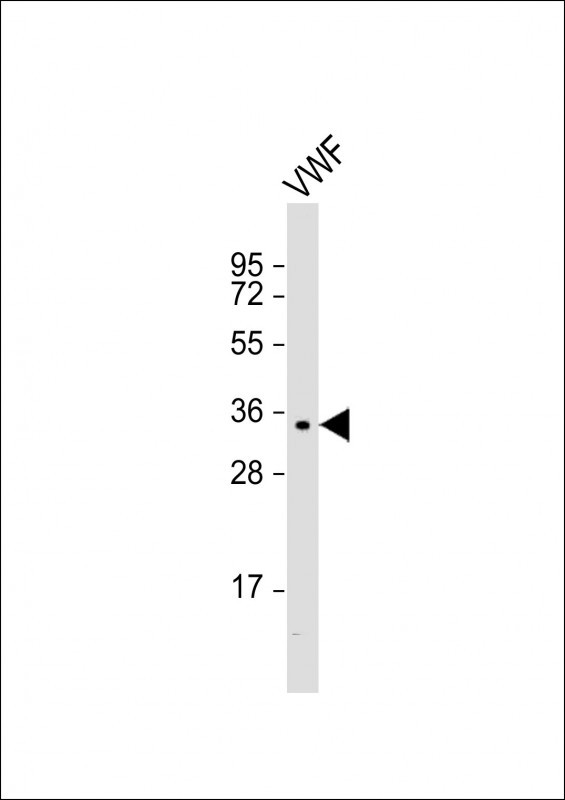
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | von Willebrand factor, vWF, von Willebrand antigen 2, von Willebrand antigen II, VWF, F8VWF |
| Entrez GeneID | 7450 |
| WB Predicted band size | 309.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with .VWF recombinant protein. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于VWF抗体的代表性文献摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Acquired von Willebrand syndrome: clinical features and laboratory characterization of autoantibodies to von Willebrand factor*
**作者**:Federici AB, et al.
**摘要**:该研究分析了获得性血管性血友病综合征(AVWS)患者的临床特征,发现其VWF抗体主要为IgG型,可特异性结合VWF的A1/A3结构域,导致VWF清除加速或功能抑制,最终引发出血症状。
2. **文献名称**:*Caplacizumab: First-in-class anti-vWF nanobody for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura*
**作者**:Scully M, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种靶向VWF A1结构域的单域抗体药物(Caplacizumab),通过阻断VWF与血小板GP1b的相互作用,快速抑制微血管血栓形成,成为治疗血栓性血小板减少性紫癜(TTP)的新型疗法。
3. **文献名称**:*Laboratory diagnosis of inhibitors to von Willebrand factor in von Willebrand disease*
**作者**:Budde U, et al.
**摘要**:提出通过混合试验、ELISA和VWF胶原结合活性检测联合诊断VWF抗体,强调抗体可能同时影响VWF抗原水平和功能,需结合多指标提高检测敏感性。
---
**备注**:文献选自权威期刊(如Blood、Haematologica),涵盖病理抗体机制、治疗性抗体药物及实验室诊断方向。如需全文链接或补充其他研究,可进一步说明。
Von Willebrand factor (VWF) antibodies are autoantibodies or alloantibodies that target VWF, a large glycoprotein critical for primary hemostasis. VWF facilitates platelet adhesion at sites of vascular injury and stabilizes coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) in circulation. Antibodies against VWF are rare but clinically significant, often leading to acquired von Willebrand syndrome (aVWS) or complicating treatment in congenital von Willebrand disease (VWD).
These antibodies can be neutralizing (inhibiting VWF function) or non-neutralizing (accelerating VWF clearance). In aVWS, autoantibodies typically develop secondary to autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus), lymphoproliferative diseases, or cardiovascular conditions. Alloantibodies may arise in severe VWD patients receiving VWF-containing therapies, impairing treatment efficacy.
Diagnosis involves assays like Bethesda tests or ELISA to detect antibody presence and quantify inhibitory activity. Clinical manifestations include mucosal bleeding, prolonged bleeding times, and low VWF antigen/FVIII levels. Management strategies vary: immunosuppression (e.g., corticosteroids, rituximab) for autoimmune cases, or bypass agents (e.g., recombinant FVIIa) for acute bleeding.
Research continues to explore antibody epitopes, mechanisms of action, and novel therapies like engineered VWF variants resistant to antibody binding. Understanding VWF antibodies is crucial for optimizing care in both acquired and inherited bleeding disorders.
×