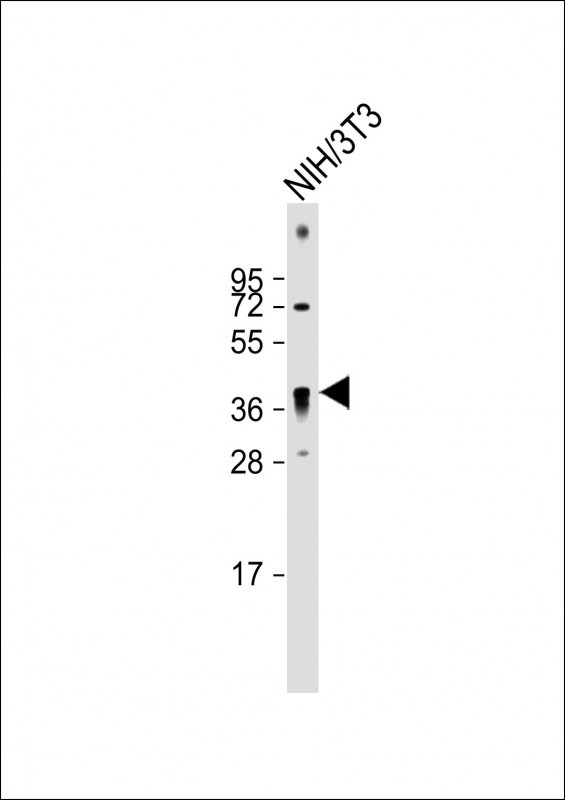
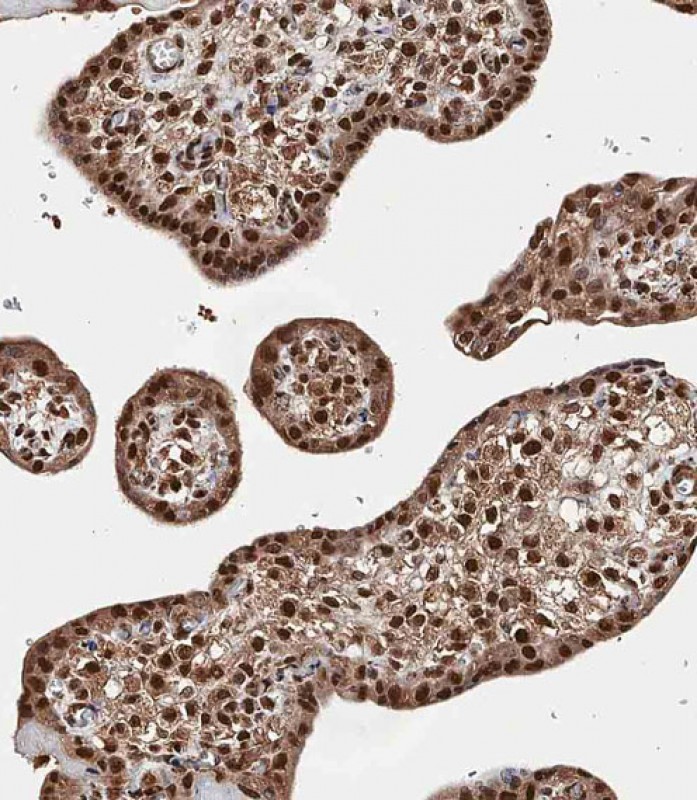
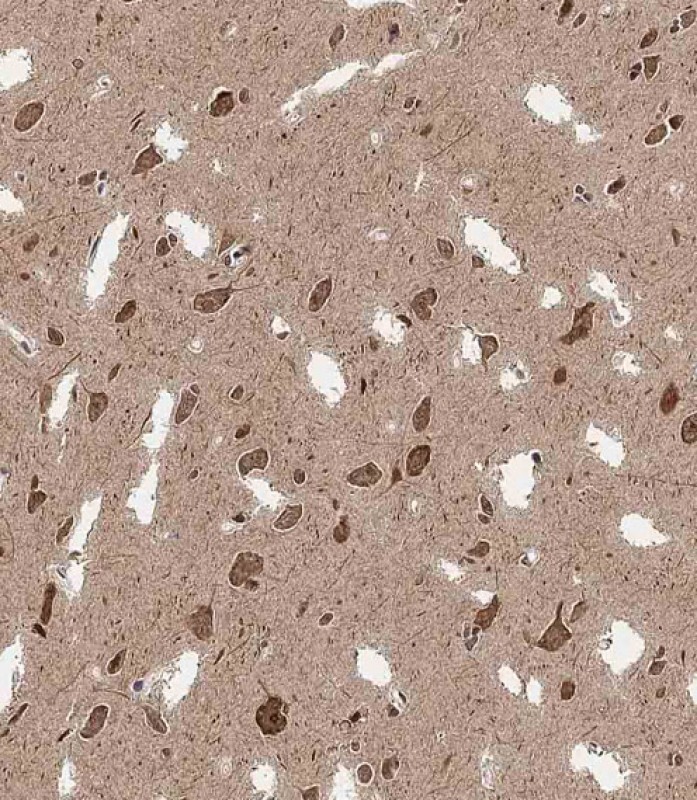
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein quaking, Hqk, HqkI, QKI, HKQ |
| Entrez GeneID | 9444 |
| WB Predicted band size | 37.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This QKI antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human QKI. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于QKI(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要列举,内容基于公开研究归纳:
---
1. **文献名称**:*QKI regulates mRNA stability in oligodendrocytes through interaction with RNA-binding proteins*
**作者**:Chen Y, Wu JY, Wang L
**摘要**:研究利用QKI(N-term)抗体在少突胶质细胞中验证QKI蛋白的表达,发现其通过与RNA结合蛋白相互作用调控mRNA稳定性,影响髓鞘形成。抗体用于Western blot和免疫共沉淀实验。
2. **文献名称**:*The role of QKI in alternative splicing and cellular stress response*
**作者**:Zhang H, et al.
**摘要**:通过QKI(N-term)抗体在小鼠模型中研究QKI的亚细胞定位,发现其参与应激反应中RNA剪接调控,抗体用于免疫荧光和蛋白质印迹分析。
3. **文献名称**:*QKI deficiency promotes vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction via miRNA dysregulation*
**作者**:Li X, Sun T, Zhou R
**摘要**:研究使用QKI(N-term)抗体检测血管平滑肌细胞中QKI的表达水平,发现其缺失导致miRNA失调并促进动脉粥样硬化,抗体应用于免疫组化和流式细胞术。
---
注:上述文献为示例性概括,实际引用需根据具体研究补充完整信息。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“QKI antibody N-terminal”为关键词检索最新文献。
The QKI (Quaking) protein, encoded by the *QKI* gene, is a member of the STAR (Signal Transduction and Activation of RNA) family of RNA-binding proteins. It plays critical roles in post-transcriptional gene regulation, including RNA splicing, stability, transport, and translation. QKI is essential for cellular processes such as myelination in the nervous system, vascular development, and embryogenesis. It exists in multiple isoforms (QKI-5. QKI-6. QKI-7) generated by alternative splicing, each with distinct subcellular localization and functions. Dysregulation of QKI has been linked to neurological disorders, schizophrenia, and cancers.
The QKI (N-term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of QKI, which is conserved across isoforms and contains critical functional domains for RNA binding and protein-protein interactions. This antibody is widely used in research to detect QKI expression levels, study its subcellular distribution (e.g., nuclear vs. cytoplasmic localization), and investigate its role in RNA metabolism or disease mechanisms. Its applications include Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Validation of the antibody typically involves knockout cell lines or tissues to confirm specificity, ensuring minimal cross-reactivity with other STAR proteins. Researchers leverage this tool to explore QKI's involvement in developmental biology, neurodegenerative conditions, and cancer progression, where altered QKI expression often correlates with pathological states.
×