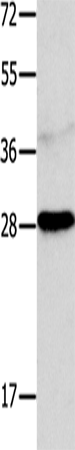
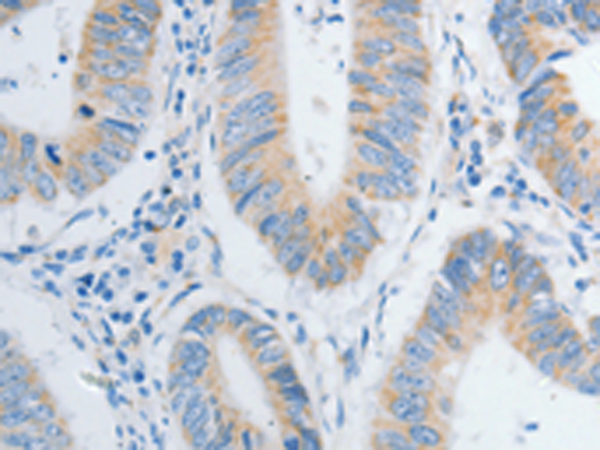
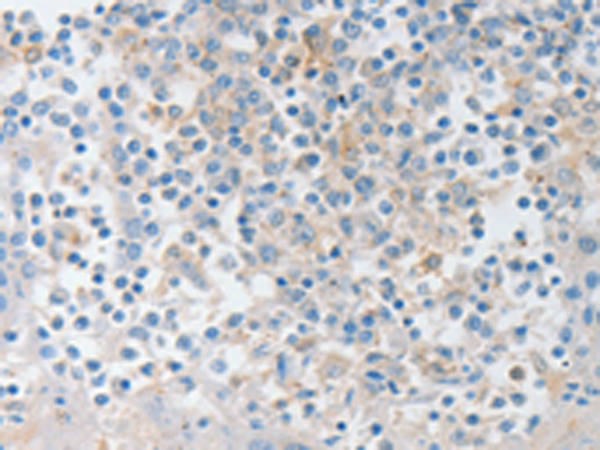
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NT4, NT5, NT-4, NT-5, NTF5, GLC10, GLC1O, NT-4/5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human NTF4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ECSCR抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下内容为示例性概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *ECSCR regulates VEGF-mediated signaling in endothelial cell migration*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了ECSCR蛋白通过调控VEGF信号通路影响内皮细胞迁移的机制,利用特异性抗体证实了ECSCR在血管生成中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Development of a monoclonal antibody against human ECSCR for cancer biomarker studies*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种高特异性抗人ECSCR单克隆抗体的开发,并通过免疫组化验证其在肿瘤血管内皮中的高表达,提示其作为癌症诊断标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *ECSCR modulates inflammatory angiogenesis in murine models*
**作者**: Patel R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用ECSCR抗体进行功能阻断实验,证明ECSCR通过调节NF-κB通路参与炎症相关血管新生,为治疗慢性炎症疾病提供新靶点。
---
*注:以上为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索关键词“ECSCR antibody”或“Endothelial Cell-Specific Chemotaxis Regulator”获取。*
The endothelial cell-specific chemotaxis regulator (ECSCR) is a transmembrane protein predominantly expressed in vascular endothelial cells, playing a critical role in regulating angiogenesis, endothelial cell migration, and vascular development. It interacts with signaling pathways like VEGF and MAPK to modulate endothelial responses during blood vessel formation. ECSCR's involvement in pathological angiogenesis, particularly in cancers and ischemic diseases, has spurred interest in developing ECSCR-targeted research tools.
ECSCR antibodies are essential reagents for detecting and quantifying ECSCR expression in experimental models. They enable studies on ECSCR's function in endothelial cell biology through techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Recent research highlights ECSCR's potential as a biomarker for tumor vasculature, driving demand for high-specificity antibodies to explore its diagnostic or therapeutic applications. Commercially available ECSCR antibodies (polyclonal or monoclonal) are often validated for cross-reactivity and application robustness, supporting both basic research and preclinical investigations into vascular-related disorders. Ongoing studies aim to clarify ECSCR's mechanistic roles and its interplay with other angiogenic regulators, further emphasizing the utility of these antibodies in advancing vascular biology and anti-angiogenic therapy development.
×