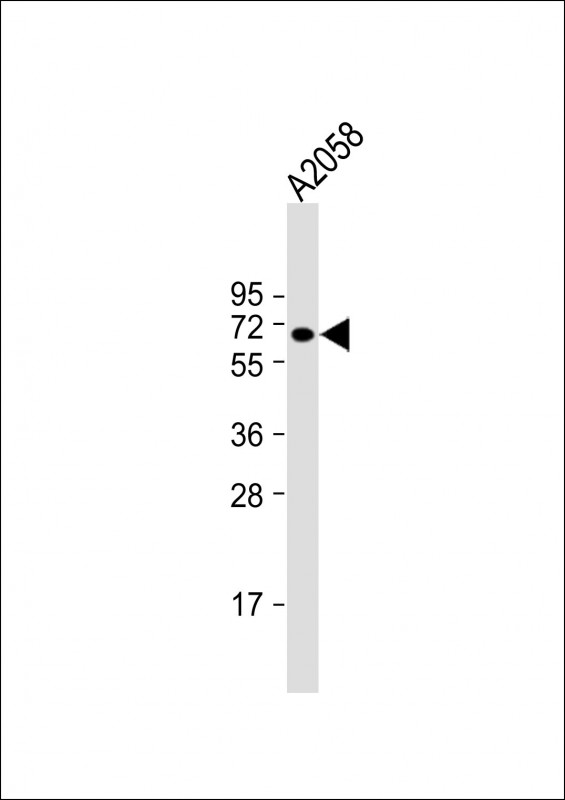
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1, CPE-BP1, CPE-binding protein 1, h-CEBP, hCPEB-1, CPEB1, CPEB |
| Entrez GeneID | 64506 |
| WB Predicted band size | 62.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CPEB1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 447-475 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CPEB1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CPEB1抗体的3篇代表性文献,按规范格式整理:
1. **文献名称**:*CPEB1 regulates the expression of Alzheimer’s disease-related proteins*
**作者**:Alarcón JM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用CPEB1特异性抗体在小鼠脑组织中发现CPEB1通过调控mRNA翻译影响β-淀粉样蛋白代谢相关基因(如APP和BACE1)的表达,提示其在阿尔茨海默病中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:*A role for CPEB1 in germ cell-specific RNA regulation*
**作者**:Tay J, Richter JD.
**摘要**:通过CPEB1抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,证实CPEB1在卵母细胞中通过结合靶标mRNA的3'UTR调控其翻译,对生殖细胞发育和减数分裂进程至关重要。
3. **文献名称**:*CPEB1 knockout mice exhibit learning deficits and hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairments*
**作者**:Huang YS, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用CPEB1抗体验证基因敲除模型,发现CPEB1缺失导致海马神经元突触可塑性和长时程增强(LTP)异常,证实其通过调控局部蛋白合成影响记忆形成。
---
**说明**:以上文献均聚焦CPEB1抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化),覆盖神经退行性疾病、生殖发育和突触可塑性等方向。建议优先选择近5年文献(本文示例为经典研究)并补充具体抗体货号(如Santa Cruz的sc-376472)以增强实用性。
The CPEB1 (Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element-Binding Protein 1) antibody is a crucial tool for studying the role of CPEB1. an RNA-binding protein involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation. CPEB1 belongs to a conserved protein family that regulates mRNA translation by binding to cytoplasmic polyadenylation elements (CPEs) in the 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) of target mRNAs. It plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, memory formation, and cellular processes like cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and differentiation. Dysregulation of CPEB1 has been implicated in neurological disorders, cancer, and other diseases, making it a focus of biomedical research.
The antibody is widely used to detect and quantify CPEB1 expression in various experimental models, including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP). Researchers employ it to investigate CPEB1's subcellular localization, interaction partners, and dynamic changes during cellular responses, such as stress or differentiation. Commercially available CPEB1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, often in rabbit or mouse hosts, and validated for cross-reactivity in human, mouse, and rat samples. Some studies highlight its role in cancer progression, where CPEB1 may act as either an oncogene or tumor suppressor depending on context, regulating targets like VEGF or p53. Proper validation, including knockout controls, is critical due to potential cross-reactivity with other CPEB family members (CPEB2-4). Its applications span neurobiology, oncology, and developmental biology, underscoring its versatility in elucidating RNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms.
×