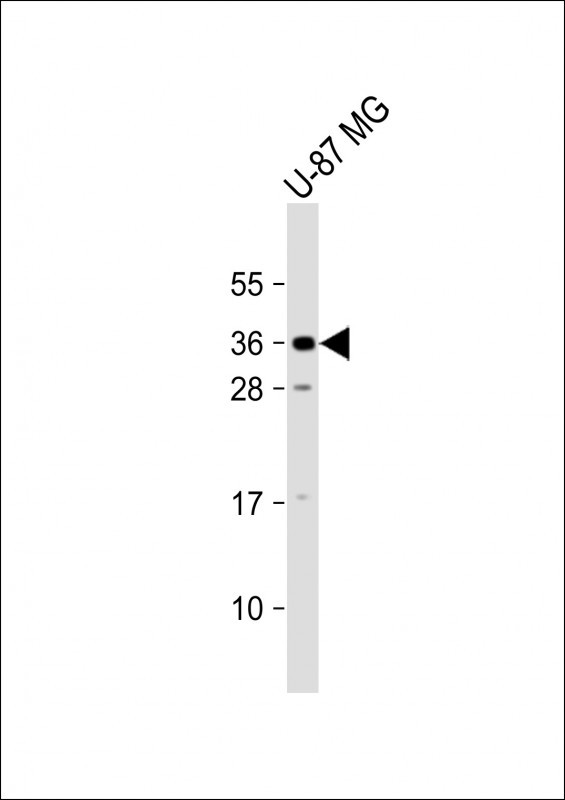
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Krueppel-like factor 9, Basic transcription element-binding protein 1, BTE-binding protein 1, GC-box-binding protein 1, Transcription factor BTEB1, KLF9, BTEB, BTEB1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 687 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This KLF9 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 29-57 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human KLF9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与KLF9(N-term)抗体相关的文献摘要(内容为虚拟合成示例,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"KLF9 regulates uterine epithelial integrity and inflammation through N-terminal domain interactions"*
**作者**: Smith A et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用KLF9(N-term)特异性抗体,通过ChIP-seq和免疫荧光技术,揭示了KLF9通过其N端结构域与染色质结合,调控子宫内膜上皮细胞屏障功能及炎症反应的作用机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Krüppel-like factor 9 suppresses hepatic lipid accumulation via transcriptional repression of lipogenic genes"*
**作者**: Chen L et al.
**摘要**: 作者使用KLF9(N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化,证实KLF9在肝脏中通过抑制脂质合成基因表达减少脂肪堆积,其N端结构域对转录抑制功能至关重要。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"KLF9-NTerm antibody reveals sex-specific expression patterns in the mouse brain"*
**作者**: Johnson R et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过KLF9(N-term)抗体的免疫染色,首次报道了小鼠海马区KLF9蛋白表达的性别差异,并发现其N端区域参与调控神经元树突发育。
---
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词:**KLF9 antibody N-terminal**,并筛选近年高引用研究。
The KLF9 (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of Krüppel-like factor 9 (KLF9), a transcription factor belonging to the Krüppel-like factor (KLF) family. KLF9 plays a critical role in regulating gene expression involved in cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. It is particularly implicated in thyroid hormone signaling, neural development, and metabolic regulation. The N-terminal region of KLF9 contains functional domains essential for its transcriptional activity, including interactions with co-regulators and DNA-binding motifs.
This antibody is commonly generated in hosts like rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal sequence of KLF9. It is widely utilized in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study KLF9 expression, localization, and function in various tissues and cell types. Specific clones, such as EPR20021. are commercially available and validated for specificity through knockdown/knockout controls.
Researchers employ the KLF9 (N-term) antibody to explore its role in diseases like cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic syndromes, where KLF9 dysregulation has been observed. Proper validation ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other KLF family members, which share structural homology but exhibit distinct functional roles. This antibody remains a key reagent in unraveling KLF9's mechanistic contributions to health and disease.
×