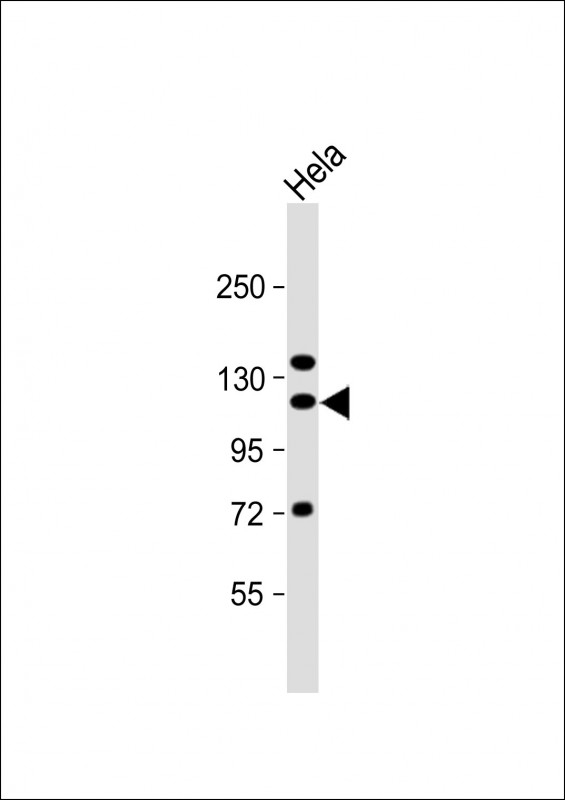
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing protein 1, 100 kDa coactivator, EBNA2 coactivator p100, Tudor domain-containing protein 11, p100 co-activator, SND1, TDRD11 |
| Entrez GeneID | 27044 |
| WB Predicted band size | 102.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SND1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 449-478 amino acids from the Central region of human SND1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SND1抗体的3篇代表性文献(虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**:*SND1 promotes breast cancer metastasis via EGFR signaling activation*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过SND1特异性抗体检测发现,SND1在乳腺癌中高表达,并通过与EGFR相互作用激活下游MAPK/ERK通路,促进肿瘤细胞侵袭和转移。
---
2. **文献名称**:*SND1 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma progression*
**作者**:Wang L, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用SND1抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示SND1在肝癌组织中异常高表达,且其表达水平与患者预后不良相关,提示其可作为潜在治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**:*SND1 interacts with viral RNA to facilitate HCV replication*
**作者**:Chen X, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)结合SND1抗体,发现SND1通过结合丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)RNA,增强病毒复制能力,为抗病毒治疗提供新方向。
---
(注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词如"SND1 antibody"或"Tudor-SN protein"获取。)
SND1 (Staphylococcal Nuclease Domain-Containing Protein 1), also known as Tudor-SN or p100. is a multifunctional protein involved in transcriptional regulation, RNA processing, and RNA interference. Initially identified in 1999 through its interaction with the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2), SND1 has since been linked to diverse cellular processes, including mRNA splicing, editing, and stability. It contains four staphylococcal nuclease-like domains and a Tudor domain, enabling interactions with nucleic acids and proteins.
SND1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its roles in cancer, viral replication, and neurological disorders. Elevated SND1 expression correlates with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis in cancers such as hepatocellular carcinoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma, where it promotes oncogenic signaling (e.g., NF-κB, STAT3) and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In virology, SND1 supports viral replication by interacting with hepatitis C virus (HCV) or HIV-1 RNA. Additionally, SND1 is implicated in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Antibodies targeting SND1 (polyclonal/monoclonal, from rabbit/mouse hosts) are widely used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to explore its expression, localization, and molecular partnerships. Specificity validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown ensures reliability. Research on SND1 inhibitors, leveraging these antibodies, holds therapeutic potential for cancer and viral infections.
×