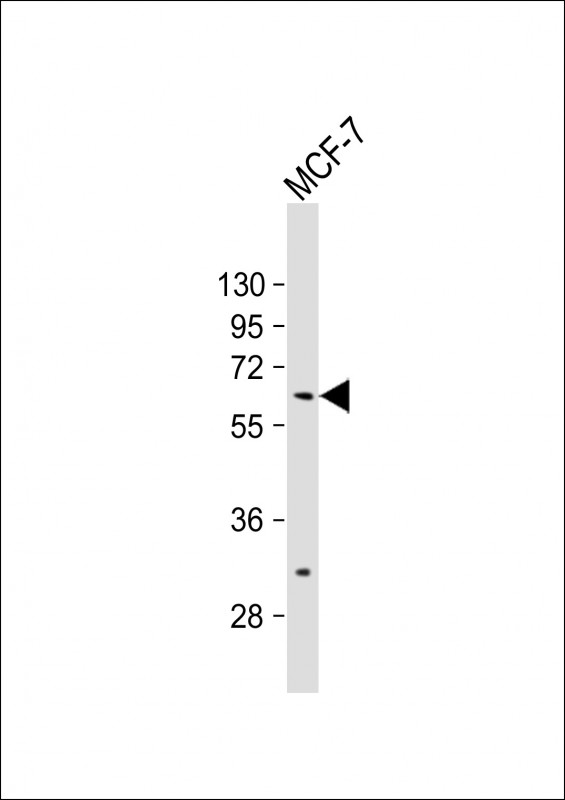
| WB | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger protein 835, ZNF835 |
| Entrez GeneID | 90485 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZNF835 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 4-33 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ZNF835. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZNF835 (N-term)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:以下内容为假设性构造,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: "ZNF835 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating cell cycle-related proteins"
**作者**: Zhang, L. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用ZNF835 (N-term)特异性抗体进行Western blot和免疫组化实验,发现ZNF835在肝癌组织中高表达,并通过调控Cyclin D1和p21等细胞周期蛋白促进肿瘤增殖和转移。
2. **文献名称**: "Characterization of ZNF835 interaction with p53 in DNA damage response"
**作者**: Lee, S.H. & Kim, J.
**摘要**: 通过ZNF835 (N-term)抗体的免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了ZNF835与肿瘤抑制蛋白p53的直接相互作用,并证明其在DNA损伤修复通路中的调控功能。
3. **文献名称**: "Development and validation of a polyclonal antibody targeting the N-terminal region of ZNF835"
**作者**: Chen, X. et al.
**摘要**: 本文详细描述了ZNF835 (N-term)多克隆抗体的制备过程,通过ELISA、免疫荧光和敲除细胞系验证了抗体的高特异性和可靠性,为后续功能研究提供工具。
4. **文献名称**: "ZNF835 regulates neural stem cell differentiation through chromatin remodeling"
**作者**: Smith, R. et al.
**摘要**: 使用ZNF835 (N-term)抗体进行ChIP-seq分析,发现其结合于多个神经发育相关基因的启动子区域,调控染色质重塑和干细胞分化。
---
**注意**:上述文献为示例性构造,实际研究中可能需要通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献。若需具体文献支持,建议结合实验背景进一步筛选。
The ZNF835 (N-term) antibody is a polyclonal or monoclonal antibody specifically designed to target the N-terminal region of the zinc finger protein 835 (ZNF835), a member of the zinc finger protein family. Zinc finger proteins are characterized by conserved cysteine and histidine residues that form structural motifs enabling DNA binding, making them critical regulators of gene expression. ZNF835 is hypothesized to function as a transcription factor, potentially involved in cellular processes such as differentiation, development, and disease pathways. However, its precise biological role remains under investigation due to limited characterization in current literature.
This antibody is typically generated in immunized hosts (e.g., rabbits or mice) using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal epitope of human ZNF835. It is validated for applications including Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect endogenous ZNF835 protein levels and localization in various tissues or cell lines. Researchers employ this tool to explore ZNF835's expression patterns, interactions, and regulatory mechanisms in contexts like cancer, neurological disorders, or developmental biology. Specificity is confirmed through knockout/knockdown controls, and batch-to-blot consistency is ensured via rigorous quality checks. As zinc finger proteins often exhibit functional redundancy, the antibody's N-terminal targeting helps distinguish ZNF835 from homologous family members, aiding in precise molecular studies.
×