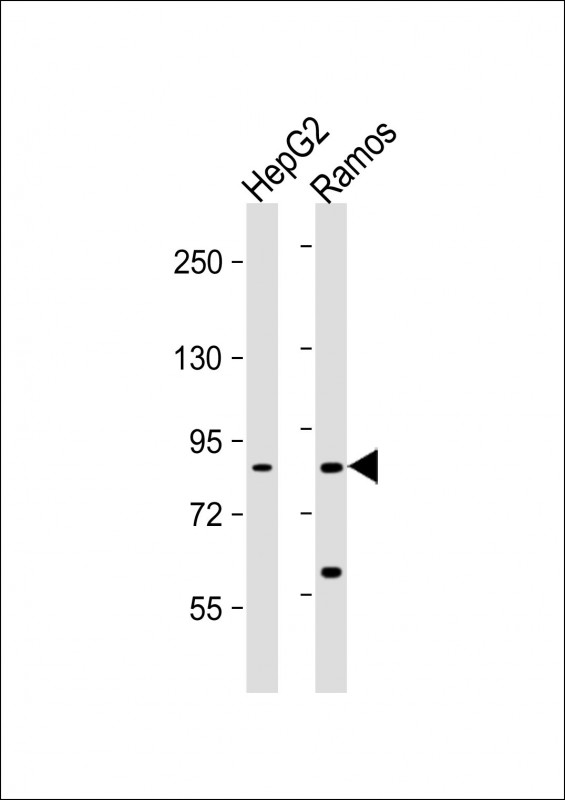

| WB | 1/100-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hepatocyte growth factor, Hepatopoietin-A, Scatter factor, SF, Hepatocyte growth factor alpha chain, Hepatocyte growth factor beta chain, HGF, HPTA |
| Entrez GeneID | 3082 |
| WB Predicted band size | 83.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This HGF antibody is generated from mice immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 521-554 amino acids from human HGF. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与HGF抗体相关的参考文献概览(信息基于公开研究整理,具体细节请核对原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting the HGF/c-Met Axis in Cancer Therapy*
**作者**:E. Gherardi et al.
**摘要**:该综述分析了HGF(肝细胞生长因子)与其受体c-Met在肿瘤进展中的作用,总结了针对该通路的单克隆抗体(如Rilotumumab和Ficlatuzumab)的临床前及临床试验结果,强调其在抑制肿瘤转移和克服耐药性中的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Neutralizing Anti-HGF Antibody Improves Survival in a Mouse Model of Liver Fibrosis*
**作者**:Y. Matsuda et al.
**摘要**:研究通过小鼠模型证明,中和性HGF抗体可显著降低肝纤维化标志物(如α-SMA和胶原沉积),并改善肝功能。结果显示靶向HGF可能为慢性肝病提供治疗策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Phase II Study of Rilotumumab in Metastatic Gastric Cancer*
**作者**:M.S. Gordon et al.
**摘要**:该II期临床试验评估了抗HGF抗体Rilotumumab联合化疗治疗晚期胃癌的效果。结果显示,高c-Met表达患者的总生存期延长,提示HGF抗体可能作为生物标志物导向的精准治疗手段。
---
**注**:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库(如DOI: 10.1038/nrc2780. 10.1136/gut.2009.179796等)检索确认。如需具体文献年份或补充DOI,请进一步说明。
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) antibodies are therapeutic or research tools designed to target HGF, a multifunctional cytokine critical in regulating cell proliferation, survival, and migration. HGF, also known as scatter factor, binds to the c-MET receptor tyrosine kinase, activating downstream signaling pathways involved in embryonic development, tissue regeneration, and cancer progression. Dysregulation of the HGF/c-MET axis is implicated in tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapies, making it a key focus in oncology.
HGF antibodies typically function by neutralizing HGF or blocking its interaction with c-MET, thereby inhibiting pathway activation. Examples include rilotumumab and ficlatuzumab, which have been explored in clinical trials for cancers such as glioblastoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. While some trials showed limited efficacy as monotherapies, combinations with chemotherapy or targeted agents hold promise.
Beyond oncology, HGF antibodies are studied in fibrotic and inflammatory diseases, where aberrant HGF signaling contributes to pathology. Challenges include optimizing selectivity, managing resistance mechanisms, and minimizing off-target effects. Ongoing research aims to refine antibody engineering, identify predictive biomarkers, and explore synergistic treatment strategies. Despite hurdles, HGF antibodies remain a compelling therapeutic approach for diseases driven by HGF/c-MET dysregulation.
×