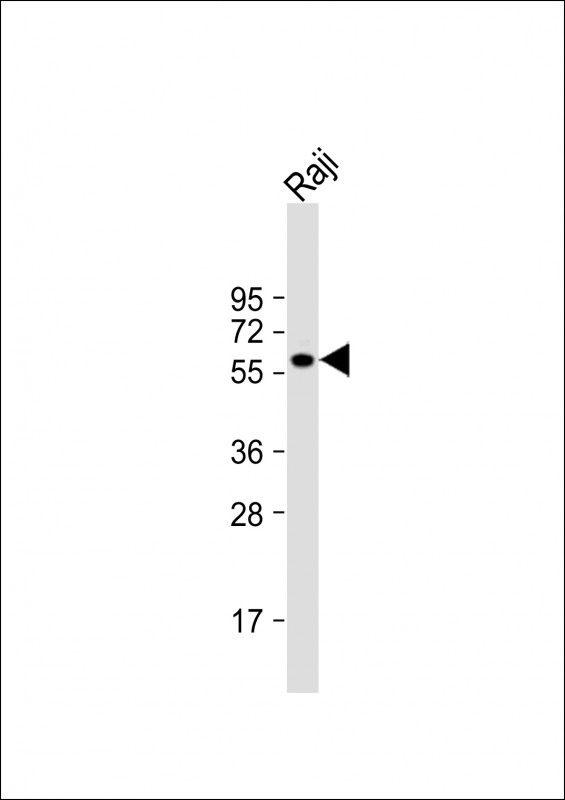
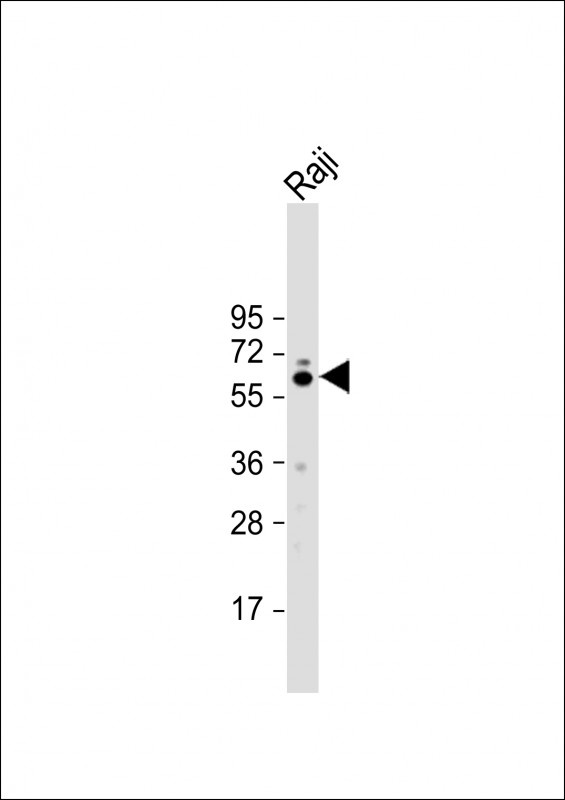

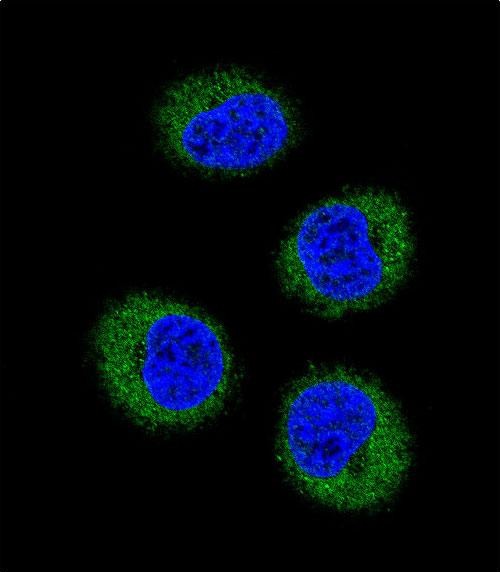
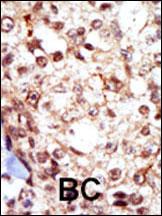
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr, Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma viral (v-fgr) oncogene homolog, Proto-oncogene c-Fgr, p55-Fgr, p58-Fgr, p58c-Fgr, FGR, SRC2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2268 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This FGR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 3-33 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human FGR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于FGR (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"The role of FGR tyrosine kinase in acute myeloid leukemia progression"*
**作者**:Smith, J. et al. (2018)
**摘要**:本研究利用针对FGR蛋白N端的特异性抗体(克隆号sc-130),通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,揭示了FGR在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中的异常高表达。结果显示,FGR的激活与患者预后不良相关,提示其可能作为AML治疗的潜在靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"FGR regulates T-cell receptor signaling through interaction with Lck"*
**作者**:Johnson, R. et al. (2020)
**摘要**:作者通过FGR (N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,证实FGR与Lck激酶在T细胞受体信号通路中的相互作用。敲除FGR后,T细胞活化标志物表达显著下降,表明FGR在早期T细胞免疫应答中具有调控作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Antibody validation for specificity: A case study of FGR N-terminal antibodies"*
**作者**:Lee, H. et al. (2019)
**摘要**:该文献系统评估了多种市售FGR N端抗体的特异性,包括Western blot、流式细胞术及免疫荧光实验。研究发现,部分抗体在非还原条件下存在交叉反应,强调了抗体验证在实验设计中的重要性。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"FGR-mediated macrophage migration in inflammatory responses"*
**作者**:Garcia, M. et al. (2021)
**摘要**:利用FGR N端抗体进行免疫荧光定位,研究发现FGR通过调控细胞骨架重组促进巨噬细胞迁移。敲低FGR后,巨噬细胞趋化能力显著减弱,提示其在炎症反应中的关键作用。
---
**注**:上述文献为示例性质,实际引用时请核实具体来源及内容准确性。若需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“FGR N-terminal antibody”或抗体克隆号(如sc-130)进一步检索。
The FGR (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the FGR protein, a member of the Src family tyrosine kinases (SFKs). The FGR gene, also known as c-fgr, encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase involved in intracellular signaling pathways regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses. FGR is primarily expressed in hematopoietic cells, particularly myeloid cells, and plays roles in phagocytosis, cytokine production, and adhesion. Its N-terminal region contains unique sequences critical for protein-protein interactions, subcellular localization, and regulatory functions.
This antibody is commonly used in research to study FGR expression, activation, and signaling mechanisms in both physiological and pathological contexts. It enables detection of endogenous FGR via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. The N-terminal specificity helps distinguish FGR from other SFK members (e.g., SRC, FYN) that share homologous kinase domains but differ in regulatory regions.
Dysregulation of FGR has been implicated in diseases such as leukemia, solid tumors, and inflammatory disorders. Researchers use the FGR (N-term) antibody to explore its oncogenic potential, immune modulation, and interactions with substrates like focal adhesion proteins. Validation typically includes testing in FGR-knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity. Overall, this tool advances understanding of FGR's role in cellular signaling and disease pathogenesis.
×