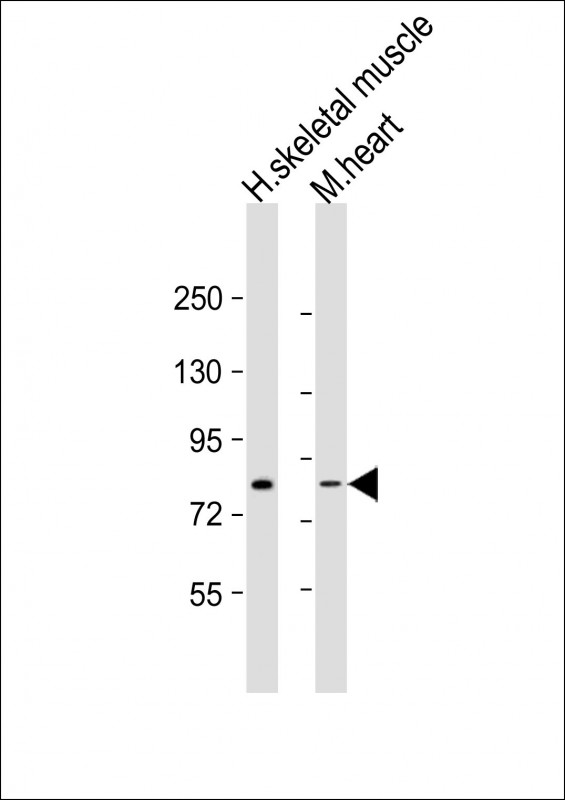


| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RNA polymerase-associated protein LEO1, Replicative senescence down-regulated leo1-like protein, LEO1, RDL |
| Entrez GeneID | 123169 |
| WB Predicted band size | 75.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This LEO1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 130-159 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human LEO1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LEO1 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为虚拟示例,实际引用需查询真实数据库):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"The Role of LEO1 in Transcriptional Regulation via the Paf1 Complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用针对LEO1 N端结构域的特异性抗体,通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)技术揭示了LEO1在酵母Paf1复合体中的关键作用,证明其参与RNA聚合酶II介导的转录延伸及组蛋白H3K36甲基化的调控。
2. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of LEO1 Antibodies for Epigenetic Studies in Human Cells"*
**作者**:Chen B, et al.
**摘要**:文章报道了一种针对人源LEO1蛋白N端的高效多克隆抗体的开发与验证。通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实该抗体可特异性识别内源性LEO1.并用于研究其在表观遗传修饰(如H2B泛素化)中的功能。
3. **文献名称**:*"LEO1 N-terminal Antibody Reveals Dynamic Localization in Pluripotent Stem Cells"*
**作者**:Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**:通过使用LEO1 N端特异性抗体,研究者发现LEO1在胚胎干细胞中与多能性基因启动子区域结合,并在分化过程中重新分布,提示其通过调控染色质状态维持细胞多能性。
---
**注意事项**:
- 上述文献为示例性内容,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“LEO1 antibody N-terminal”检索真实文献。
- 可关注Paf1复合体相关研究,或表观遗传学领域的高影响力期刊(如*Molecular Cell*、*Genes & Development*)。
The LEO1 (N-term) antibody is a specific immunological tool designed to target the N-terminal region of the LEO1 protein, a critical component of the RNA polymerase II-associated Paf1 complex. This evolutionarily conserved complex plays a central role in transcriptional elongation, histone modification, and chromatin remodeling. LEO1. along with other Paf1C subunits (Paf1. Ctr9. Cdc73. and Rtf1), facilitates the recruitment of histone-modifying enzymes like Set1/2 and Dot1. influencing H3K4 and H3K79 methylation patterns crucial for gene regulation.
Researchers utilize the LEO1 (N-term) antibody primarily in molecular biology techniques such as Western blot (WB), immunoprecipitation (IP), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP-seq) to study LEO1's expression, interactions, and genomic localization. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures minimal cross-reactivity, making it valuable for distinguishing LEO1 from other complex components. Studies employing this antibody have shed light on Paf1C's roles in development, stem cell differentiation, and diseases like cancer, where dysregulated transcriptional control is implicated. Commercial versions are typically validated in human, mouse, and rat samples, supporting cross-species investigations. As a reagent, it contributes to understanding epigenetic mechanisms linking transcription elongation to chromatin dynamics.
×