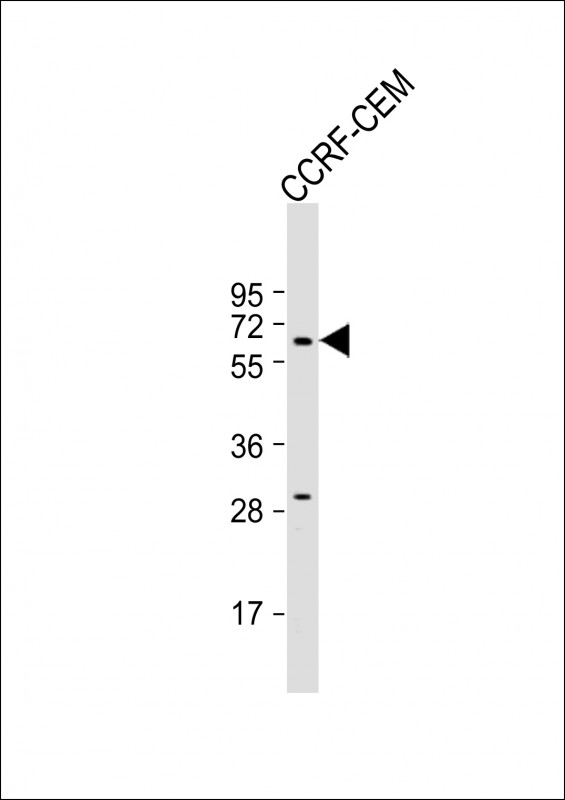
| WB | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Dystrotelin, DYTN |
| Entrez GeneID | 391475 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This DYTN antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 419-447 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human DYTN. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DYT1(TOR1A基因)抗体的研究文献示例(因“DYTN”可能存在拼写混淆,暂按DYT1相关研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Immunohistochemical localization of torsinA in nonhuman primate brains*
**作者**: Konakova M, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过特异性抗体检测TOR1A蛋白在灵长类脑组织中的分布,揭示其在基底神经节和皮质区域的表达模式,支持其在神经发育中的作用。
2. **文献名称**: *TorsinA antigen distribution in cultured cells*
**作者**: Walker RH, et al.
**摘要**: 利用抗TOR1A抗体分析细胞模型中蛋白定位,发现其在核膜和内质网的异常聚集可能与DYT1型肌张力障碍的病理机制相关。
3. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based therapy in a murine model of DYT1 dystonia*
**作者**: Bragg DC, et al.
**摘要**: 在小鼠模型中测试靶向TOR1A的抗体疗法,发现其可减少突变蛋白聚集并改善运动功能,为治疗提供潜在策略。
---
**注意**:若您所指“DYTN”为特定抗体名称或新型靶点,建议核实术语准确性。上述文献聚焦于DYT1/TOR1A相关研究,更多文献可通过PubMed以关键词“TOR1A antibody”或“DYT1 dystonia”进一步检索。
**Background of DYTN Antibodies**
DYTN antibodies are specialized immunoreagents associated with research on neurological disorders, particularly dystonias—movement disorders characterized by sustained muscle contractions and abnormal postures. While the term "DYTN" is not universally standardized, it likely references antibodies targeting proteins linked to dystonia-related genetic mutations (e.g., *TOR1A* in DYT1 dystonia). These antibodies are critical for detecting and studying proteins involved in neuronal signaling, synaptic function, or cellular stress responses implicated in dystonia pathogenesis.
Research suggests dystonias arise from dysfunctional neural circuits in the basal ganglia, cerebellum, or sensorimotor cortex. Antibodies against dystonia-associated proteins (e.g., torsinA in DYT1) enable visualization of protein localization, expression levels, and interactions in cellular or animal models. This aids in understanding mechanisms like misfolded protein aggregation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, or disrupted dopamine signaling.
Clinically, DYTN antibodies may assist in diagnostic assays or biomarker discovery, though their utility remains primarily experimental. Challenges include heterogeneity in dystonia subtypes and limited consensus on specific molecular targets. Ongoing studies aim to refine antibody specificity and explore therapeutic applications, such as targeting pathogenic proteins via immunotherapy. Overall, DYTN antibodies represent a niche but vital tool in unraveling the molecular complexity of dystonias.
×