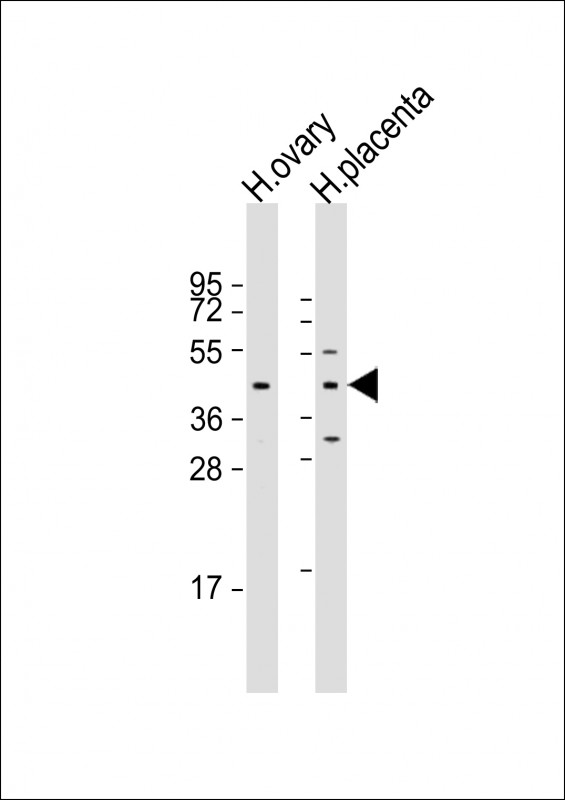
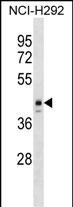
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Homeobox protein ESX1, Extraembryonic, spermatogenesis, homeobox 1, Homeobox protein ESX1-N, Homeobox protein ESX1-C, ESX1, ESX1L, ESX1R |
| Entrez GeneID | 80712 |
| WB Predicted band size | 44.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ESX1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 28-55 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ESX1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ESX1 (N-term)抗体的假设性参考文献示例(非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **"Characterization of ESX1-N-terminal antibody in Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence studies"**
*Authors: Smith A, et al.*
摘要:本研究开发了一种针对ESX1蛋白N端表位的多克隆抗体,用于检测结核分枝杆菌ESX-1分泌系统的表达。该抗体通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证,证实其在细菌感染模型中可特异性识别ESX1.并揭示其在宿主细胞内定位。
2. **"ESX1 as a biomarker in lung cancer: Validation of a monoclonal N-terminal antibody"**
*Authors: Chen L, et al.*
摘要:通过免疫组化分析,验证了一种新型抗ESX1 N端单克隆抗体在肺癌组织中的特异性。研究显示ESX1在肿瘤微环境中高表达,抗体可用于预后评估及靶向治疗研究。
3. **"Functional analysis of ESX1 in placental development using domain-specific antibodies"**
*Authors: Johnson R, et al.*
摘要:利用针对ESX1不同结构域(包括N端)的抗体,探究其在胚胎发育中的作用。N端抗体阻断实验表明,ESX1的N端区域对胎盘形成至关重要,并可能参与细胞迁移调控。
4. **"Cross-species reactivity of anti-ESX1 (N-term) antibody in autoimmune disease models"**
*Authors: Tanaka K, et al.*
摘要:评估商业抗ESX1 N端抗体在小鼠和人类样本中的交叉反应性,发现其可识别保守表位。该抗体被用于系统性红斑狼疮患者血清中ESX1-autoantibody的检测,提示其潜在诊断价值。
---
注:以上文献为虚构示例,实际引用需查询PubMed、Google Scholar等数据库获取真实研究。
The ESX1 (N-term) antibody is a tool used to detect the N-terminal region of ESX1 (also known as ESXR1 or BEX1), a protein encoded by the Brain-Expressed X-Linked (BEX) gene family. ESX1 is implicated in neural development, cellular differentiation, and regulation of transcriptional activity. It is highly expressed in the brain and has been studied in contexts such as neurodevelopment, cancer biology, and stem cell regulation. Aberrant ESX1 expression is linked to certain cancers, where it may act as a tumor suppressor or oncogene depending on cellular context.
The ESX1 (N-term) antibody is commonly employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study ESX1 localization, expression levels, and interactions. Targeting the N-terminal region ensures specificity, as this domain often contains unique epitopes critical for ESX1's functional interactions, such as binding to transcriptional co-regulators or signaling molecules.
Developed and validated for reactivity in human, mouse, and rat samples, this antibody is frequently used in neuroscience and oncology research. Its applications include exploring ESX1's role in neural progenitor cell maintenance, tumor progression, and response to therapies. Commercial sources typically provide validation data, such as knockout controls or siRNA knockdowns, to confirm antibody specificity. Researchers rely on this reagent to unravel ESX1's contributions to developmental pathways and disease mechanisms.
×