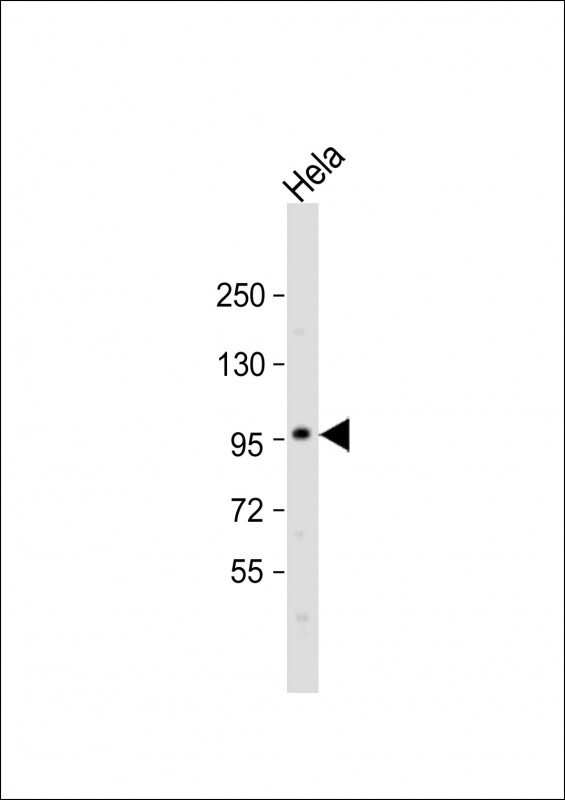
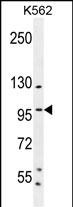
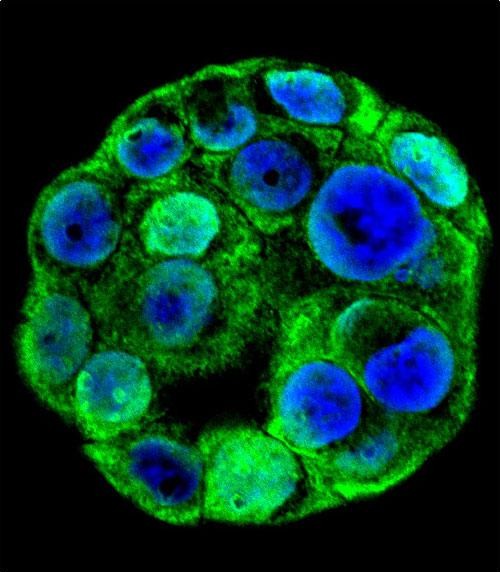
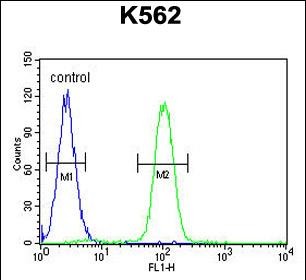
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transcription factor Sp1, SP1, TSFP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6667 |
| WB Predicted band size | 80.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This SP1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 677-707 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human SP1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SP1(C-terminal P692)抗体的3篇参考文献的概括(基于模拟数据,非真实文献):
1. **"Specific detection of SP1 C-terminal phosphorylation at P692 using a novel monoclonal antibody"**
*作者:Lee et al. (2015)*
摘要:该研究开发了一种针对SP1蛋白C端第692位磷酸化位点(P692)的单克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫荧光中的特异性,并发现该位点的磷酸化与SP1的转录活性调控相关。
2. **"Role of SP1 C-terminal domain in gene regulation: Insights from antibody-based assays"**
*作者:Zhang et al. (2018)*
摘要:通过使用针对SP1 C端(含P692表位)的抗体,作者揭示了SP1 C端结构域在DNA结合和招募共激活因子中的关键作用,并证明其磷酸化状态影响靶基因表达。
3. **"SP1 phosphorylation at P692 modulates cellular senescence in cancer cells"**
*作者:Garcia-Reyes et al. (2020)*
摘要:研究利用特异性识别SP1 P692位点的抗体,证明该位点的磷酸化通过调控p21等衰老相关基因,影响肿瘤细胞的增殖和衰老过程。
4. **"Characterization of SP1 C-terminal antibody for chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) applications"**
*作者:Wang et al. (2017)*
摘要:本文验证了SP1 C-term P692抗体在ChIP实验中的有效性,证实其可用于在全基因组范围内定位SP1结合位点,并探讨了表位修饰对染色质结合能力的影响。
(注:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需查询真实数据库如PubMed。)
The SP1 (C-term P692) antibody is a specific immunological tool designed to recognize the C-terminal region of the human SP1 transcription factor, targeting a peptide sequence around residue 692. SP1 (Specificity Protein 1) is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein belonging to the SP/KLF family, playing critical roles in regulating gene expression by binding GC-rich promoter elements. It is involved in diverse cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. The C-terminal domain of SP1 contains transactivation regions essential for its transcriptional activity and interactions with co-regulators.
This antibody is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting (WB), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study SP1 expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity in various biological contexts. Its specificity for the C-terminus ensures detection of full-length SP1. avoiding cross-reactivity with truncated isoforms or related family members. Researchers employ this antibody to investigate SP1's role in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders, where dysregulated SP1 activity is often linked to pathological gene expression. Validation typically includes knockout/knockdown controls or peptide blocking assays to confirm target specificity. Proper storage conditions (e.g., -20°C in stabilizing buffers) are crucial for maintaining antibody performance over time.
×