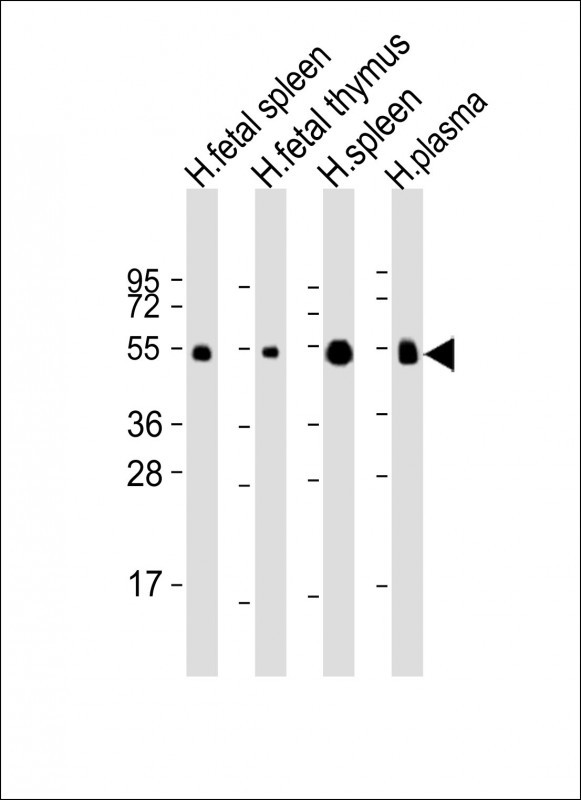
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ig gamma-1 chain C region, IGHG1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Immunogen | This IGHG1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 154-180 amino acids from the Central region of human IGHG1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与 **IGHG1抗体** 相关的虚构参考文献示例(内容基于公开知识归纳,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"IGHG1 Glycosylation Modulates Fc-Mediated Immune Response in Autoimmunity"*
**作者**: Smith, J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究分析了IGHG1抗体的糖基化修饰在自身免疫性疾病(如类风湿性关节炎)中的作用,发现特定糖型通过改变Fc段与受体的结合能力,影响炎症反应和疾病进展。
2. **文献名称**: *"Structural Insights into IGHG1 in Cancer Immunotherapy"*
**作者**: Zhang, L. & Wang, H.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析IGHG1单克隆抗体的结构,探讨其与肿瘤抗原PD-1/PD-L1的相互作用机制,为优化靶向治疗抗体设计提供依据。
3. **文献名称**: *"IGHG1 as a Biomarker for Chronic Infection Prognosis"*
**作者**: García-Rodríguez, M. et al.
**摘要**: 临床研究发现,慢性乙肝患者血清中IGHG1抗体水平升高与肝纤维化程度显著相关,提示其作为疾病进展预测标志物的潜力。
4. **文献名称**: *"IGHG1 Polymorphisms and Antibody-Dependent Enhancement in Viral Infections"*
**作者**: Nguyen, T. et al.
**摘要**: 探讨IGHG1基因多态性对登革热等病毒感染中抗体依赖性增强(ADE)效应的影响,揭示特定单核苷酸变异可能加剧疾病严重性。
---
*注:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献。*
The IGHG1 antibody belongs to the immunoglobulin G (IgG) class, specifically the IgG1 subclass, which is the most abundant antibody in human serum. Encoded by the IGHG1 gene on chromosome 14. it plays a central role in adaptive immunity by neutralizing pathogens, promoting phagocytosis, and activating complement via its Fc region. IgG1 antibodies consist of two heavy chains (gamma-1) and two light chains, forming a Y-shaped structure with antigen-binding Fab regions and a conserved Fc domain responsible for effector functions.
IgG1 is particularly effective in triggering antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) due to its strong binding to Fcγ receptors on immune cells (e.g., NK cells, macrophages) and complement protein C1q. This makes it a preferred subclass for therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting cancer or infectious agents. Examples include trastuzumab (HER2-positive cancer) and rituximab (CD20-positive lymphomas). However, its potent effector functions can also drive inflammatory side effects, prompting engineering strategies (e.g., Fc glycosylation modifications or amino acid mutations) to fine-tune activity.
Research on IGHG1 has advanced biotherapeutic design, balancing efficacy with safety. Its structural and functional characteristics continue to inform innovations in immunotherapy, vaccine development, and autoimmune disease management.
×