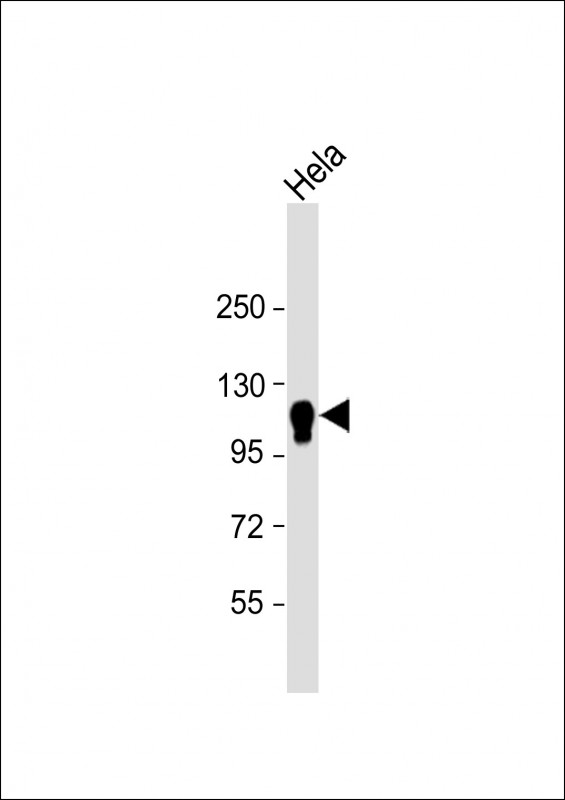
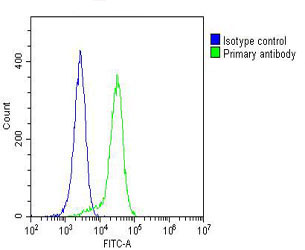
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase CYLD, 3.4.19.12, Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD, Ubiquitin thioesterase CYLD, Ubiquitin-specific-processing protease CYLD, CYLD, CYLD1, KIAA0849 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1540 |
| WB Predicted band size | 107.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CYLD antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 305-582 amino acids from human CYLD. |
+ +
以下是关于CYLD抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"CYLD regulates spindle orientation by stabilizing astral microtubules and promoting dishevelled-NUMA-dynein/dynactin complex formation"**
*作者:Yang, Y., et al.*
摘要:该研究利用CYLD特异性抗体进行免疫荧光和共聚焦显微镜分析,发现CYLD通过稳定星体微管并促进Dvl-NUMA-Dynein复合物的形成,调控细胞分裂时的纺锤体定向,揭示了CYLD在细胞周期中的新功能。
2. **"CYLD inhibits tumorigenesis and metastasis by blocking IκB kinase-dependent NF-κB activation"**
*作者:Hellerbrand, C., et al.*
摘要:通过Western blot和免疫组化分析CYLD表达,研究发现CYLD通过抑制IKK介导的NF-κB信号通路,抑制肿瘤生长和转移,为CYLD作为肿瘤抑制因子提供了机制证据。
3. **"Deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by disassembling linear ubiquitin chains"**
*作者:Tauriello, D.V.F., et al.*
摘要:该文献采用CYLD抗体进行免疫沉淀和质谱分析,证明CYLD通过去泛素化线性泛素链抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,为CYLD在发育和癌症中的调控作用提供了分子机制。
4. **"CYLD deficiency causes genomic instability in T cells and promotes lymphomagenesis"**
*作者:Staal, J., et al.*
摘要:利用CYLD敲除小鼠模型及免疫印迹技术,研究发现CYLD缺失导致T细胞基因组不稳定并促进淋巴瘤发生,强调了CYLD在维持淋巴细胞稳态中的关键作用。
这些文献展示了CYLD抗体在细胞生物学、肿瘤机制及免疫调节等研究中的应用,涵盖Western blot、免疫荧光、免疫组化等多种实验方法。
CYLD antibody is a key tool for studying the CYLD gene product, a tumor suppressor protein encoded by the *CYLD* gene. CYLD functions as a deubiquitinating enzyme that regulates critical signaling pathways, including NF-κB, JNK, and Wnt/β-catenin, by removing lysine 63-linked ubiquitin chains from specific substrates. Initially identified through its association with familial cylindromatosis (a rare autosomal dominant disorder causing skin tumors), CYLD’s role extends to modulating inflammation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation or mutations in CYLD are linked to various cancers (e.g., skin, colon, and renal cancers) and inflammatory conditions.
CYLD antibodies are widely used in research to detect CYLD expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. They help elucidate CYLD’s molecular interactions, subcellular localization, and tissue-specific roles. Commercially available antibodies target distinct epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions), enabling diverse applications. Recent studies also explore CYLD’s involvement in immune responses, metabolic regulation, and resistance to chemotherapy, highlighting its therapeutic potential.
Validation of CYLD antibodies is crucial due to potential cross-reactivity or variability in isoforms. Their utility spans basic research, biomarker discovery, and preclinical studies, making them essential for understanding CYLD’s multifaceted biological impact.
×