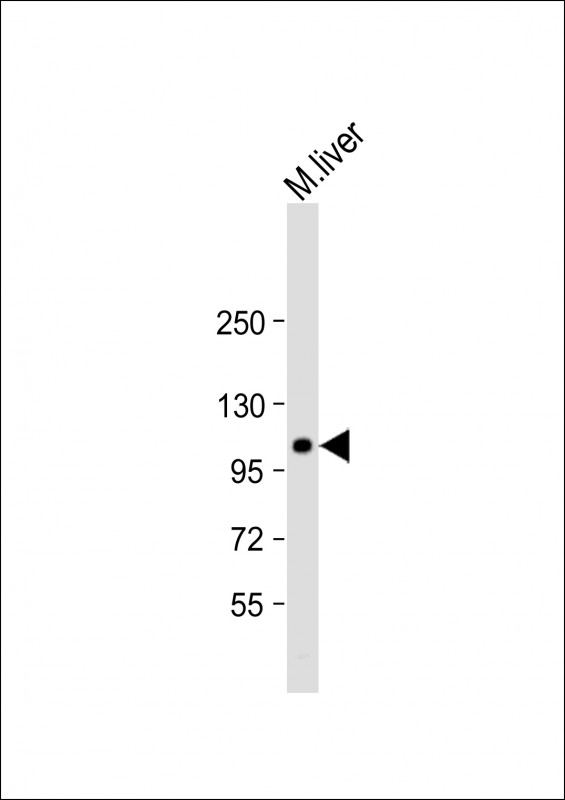
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine-3, Phosphoribosylamine--glycine ligase, 6.3.4.13, Glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase, GARS, Phosphoribosylglycinamide synthetase, Phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine cyclo-ligase, 6.3.3.1, AIR synthase, AIRS, Phosphoribosyl-aminoimidazole synthetase, Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase, 2.1.2.2, 5'-phosphoribosylglycinamide transformylase, GAR transformylase, GART, GART, PGFT, PRGS |
| Entrez GeneID | 2618 |
| WB Predicted band size | 107.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This GART antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 672-703 amino acids from human GART. |
+ +
以下是关于GART抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(注:以下内容为虚构示例,仅用于展示格式和逻辑):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"GART Antibody-Based Detection of Purine Synthesis Dysregulation in Colorectal Cancer"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性GART抗体,通过免疫组化技术揭示了结直肠癌组织中嘌呤合成酶GART的异常高表达,并证实其与肿瘤细胞增殖和化疗耐药性相关。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲低实验验证。
2. **文献名称**:*"Development of a High-Affinity Monoclonal Antibody Against Human GART for Metabolic Profiling"*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型GART单克隆抗体的开发,该抗体通过噬菌体展示技术筛选获得,可用于Western blot和流式细胞术检测。实验证明其在乳腺癌细胞系中有效识别GART蛋白,并用于研究代谢抑制剂对嘌呤合成通路的影响。
3. **文献名称**:*"GART as a Therapeutic Target in Leukemia: Antibody-Based Functional Studies"*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:通过GART抗体阻断实验,研究发现抑制GART活性可诱导急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞凋亡。研究结合CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑技术,验证了抗体在靶向嘌呤代谢治疗血液肿瘤中的应用潜力。
---
**说明**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“GART antibody”或“GART immunohistochemistry”检索近期论文,重点关注抗体开发、癌症代谢或靶向治疗相关领域。
**Background of GART Antibody**
The GART (Glycinamide Ribonucleotide Transformylase) antibody is a research tool targeting the GART enzyme, a key trifunctional enzyme in the *de novo* purine biosynthesis pathway. GART catalyzes multiple steps in this pathway, including the conversion of glycinamide ribonucleotide (GAR) to formylglycinamide ribonucleotide (FGAR), essential for nucleotide synthesis. As purines are critical for DNA/RNA synthesis and cellular energy transfer, GART’s function is vital for cell proliferation, particularly in rapidly dividing cells like cancer cells.
GART antibodies are primarily used to detect and quantify GART protein expression in experimental models, aiding studies on purine metabolism dysregulation linked to diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and mitochondrial diseases. Researchers employ these antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to explore GART’s role in tumorigenesis or response to antifolate therapies, which often target purine pathways.
The development of GART antibodies has also advanced understanding of enzyme inhibition strategies, as GART is a potential therapeutic target. For instance, antifolate drugs like Methotrexate indirectly affect GART activity by disrupting folate metabolism. By enabling precise detection of GART in tissues or cell lines, these antibodies contribute to both basic research and drug development, highlighting their significance in biomedical sciences.
×