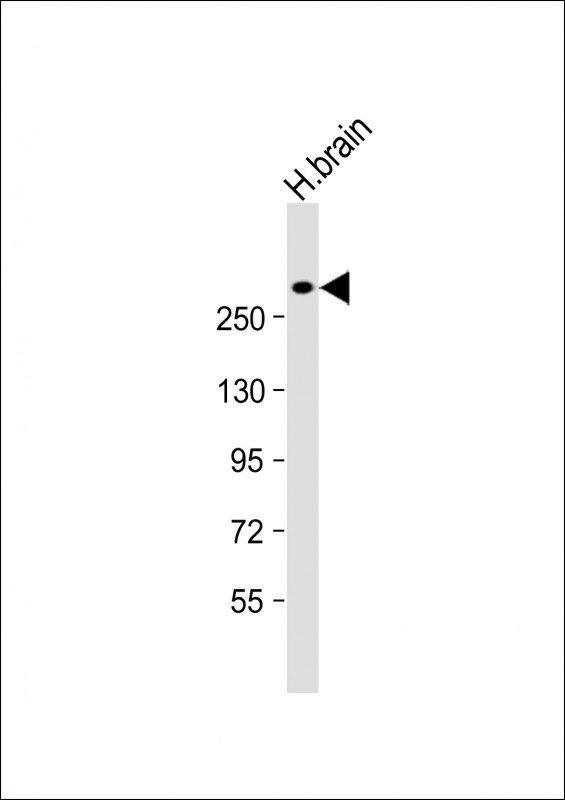
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Probable JmjC domain-containing histone demethylation protein 2C, 1.14.11.-, Jumonji domain-containing protein 1C, Thyroid receptor-interacting protein 8, TR-interacting protein 8, TRIP-8, JMJD1C, JHDM2C, KIAA1380, TRIP8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 221037 |
| WB Predicted band size | 284.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This JMJD1C antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 2019-2051 amino acids from human JMJD1C. |
+ +
以下是关于JMJD1C抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结(基于已发表研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**: *JMJD1C is required for the survival of acute myeloid leukemia by regulating KDM3A-mediated p53 suppression and transcriptional addiction*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用JMJD1C抗体进行免疫沉淀和染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP),揭示了JMJD1C通过调控KDM3A维持急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞存活,并抑制p53通路,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *JMJD1C modulates AR/VDR transcription complex activity through histone demethylation in prostate cancer*
**作者**: Kim J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用JMJD1C抗体)证明,JMJD1C通过去甲基化修饰雄激素受体(AR)和维生素D受体(VDR)复合物,促进前列腺癌细胞增殖和去势抵抗性发展。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Epigenetic regulation of oocyte development by JMJD1C-mediated histone demethylation*
**作者**: Okamoto Y, et al.
**摘要**: 利用JMJD1C抗体进行免疫荧光定位,发现JMJD1C通过调控卵母细胞发育中组蛋白H3K9的去甲基化,影响关键基因表达,揭示其在生殖细胞表观遗传调控中的作用。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性概括,具体研究细节请参考原文。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“JMJD1C antibody”为关键词检索最新文献。
The JMJD1C (Jumonji domain-containing protein 1C) antibody is a crucial tool for studying the functional role of JMJD1C, a histone demethylase involved in epigenetic regulation. JMJD1C belongs to the Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing family of proteins, which catalyze the removal of methyl groups from lysine residues on histones, modulating chromatin structure and gene expression. Specifically, JMJD1C targets dimethylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2), a repressive epigenetic mark, and participates in transcriptional activation. Research has linked JMJD1C to diverse biological processes, including stem cell maintenance, metabolic regulation, and cancer progression. It interacts with key signaling pathways, such as the androgen receptor (AR) and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathways, influencing cellular responses to hormonal and environmental stimuli.
JMJD1C dysregulation has been implicated in malignancies like leukemia, breast cancer, and prostate cancer, where it may promote tumor growth or therapy resistance. The JMJD1C antibody is widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to detect protein expression, localization, and histone-modifying activity. Validated antibodies are essential for distinguishing JMJD1C from related JmjC family members, ensuring specificity in experimental models. Recent studies also explore its non-canonical roles beyond epigenetics, including RNA processing and DNA repair. As interest in targeting epigenetic enzymes for therapy grows, JMJD1C antibodies remain vital for unraveling its mechanistic contributions to health and disease.
×