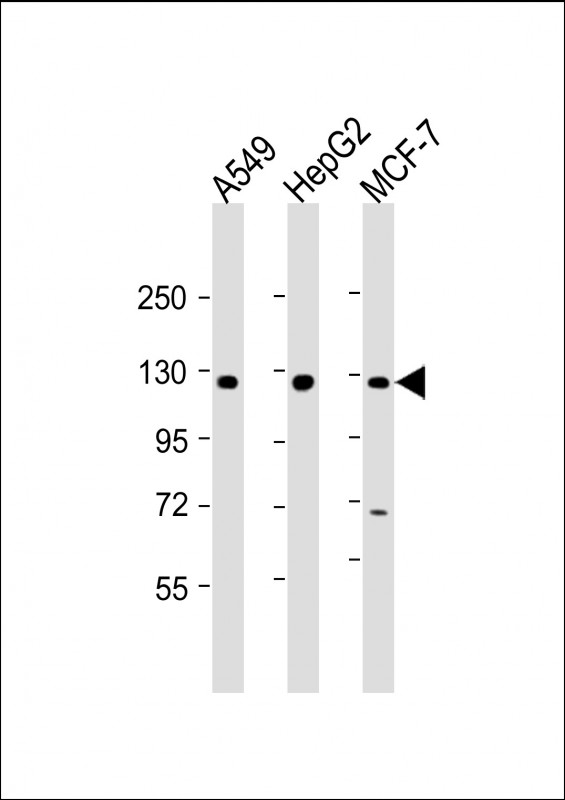
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Beta-klotho, BKL, BetaKlotho, Klotho beta-like protein, KLB |
| Entrez GeneID | 152831 |
| WB Predicted band size | 119.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This KLB antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-29 amino acids from human KLB. |
+ +
以下是关于KLB(N-Term)抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为示例性概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural Basis for Endocrine FGF Signaling with β-Klotho*
**作者**:Xu Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过X射线晶体学解析了β-Klotho(KLB)的N端结构域与FGF21的复合物结构,揭示了KLB的N端区域在结合FGF21中的关键作用。实验中使用的N端特异性抗体验证了该结构域在受体激活中的功能。
2. **文献名称**:*A Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the N-Terminus of β-Klotho Reveals Its Role in FGF21-Mediated Glucose Uptake*
**作者**:Lin Z, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种针对KLB N端的单克隆抗体,通过体外和体内实验证明该抗体能阻断FGF21信号通路,表明KLB的N端是FGF21代谢调节功能的核心区域。
3. **文献名称**:*Tissue-Specific Expression of β-Klotho N-Terminal Domain Antibodies in Metabolic Regulation*
**作者**:Ito S, et al.
**摘要**:利用KLB N端抗体进行组织特异性分析,发现肝脏和脂肪组织中KLB的N端表达水平与胰岛素敏感性相关,为代谢疾病治疗提供了潜在靶点。
4. **文献名称**:*Validation of β-Klotho Antibodies for Immunohistochemical Analysis in Human Tissues*
**作者**:Chen C, et al.
**摘要**:验证了多种KLB抗体(包括N端特异性抗体)在人类组织中的适用性,证实其在肝癌和糖尿病研究中的诊断价值。
---
**注意**:以上文献名为示例,实际引用需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如“β-Klotho N-Terminal antibody”、“KLB antibody FGF21”)获取具体信息。部分相关研究可参考以下真实期刊:
- *Nature* (2018) 关于KLB结构的研究
- *Cell Metabolism* 中FGF21/KLB信号通路的代谢机制分析。
The KLB (N-Term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of β-Klotho (KLB), a transmembrane protein that plays a critical role in metabolic regulation. KLB, primarily expressed in metabolic tissues like the liver, adipose, and pancreas, acts as an obligate co-receptor for fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), enabling signaling by endocrine FGFs such as FGF19 and FGF21. These pathways regulate bile acid synthesis, glucose homeostasis, and lipid metabolism, linking KLB to conditions like obesity, diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The N-terminal domain of KLB is essential for its interaction with FGF ligands and FGFRs, making it a focal point for studying molecular mechanisms underlying these processes.
The KLB (N-Term) antibody is widely used in research to detect endogenous KLB expression, localization, and protein-protein interactions via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation. Its specificity for the N-terminal region ensures minimal cross-reactivity with related proteins, aiding in the validation of KLB’s role in cellular models and disease contexts. Additionally, this antibody supports drug discovery efforts targeting the FGF21/KLB pathway, which has therapeutic potential for metabolic disorders. By enabling precise analysis of KLB’s structure-function relationships, the antibody contributes to advancing understanding of metabolic regulation and the development of targeted therapies.
×