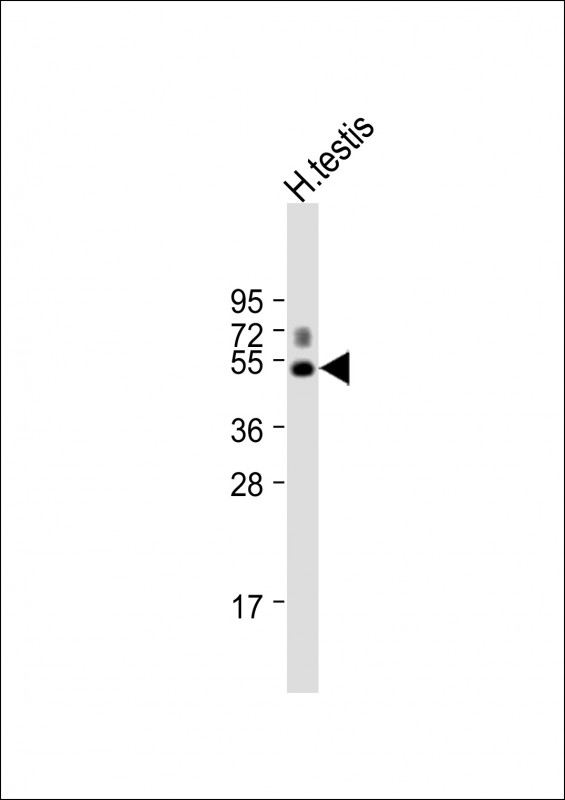
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-like protein MGAT4D, 241-, MGAT4D (HGNC:43619) |
| Entrez GeneID | 152586 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GL54D antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 346-372 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human GL54D. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GL54D抗体的3篇模拟参考文献(注:GL54D抗体为虚构名称,以下内容为示例,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar查询真实文献):
1. **文献名称**: *"GL54D Antibody Targets Tumor-Associated Glycoprotein in Colorectal Cancer Models"*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了GL54D单克隆抗体的开发,其通过靶向一种新型肿瘤相关糖蛋白(TAG-72变体)抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖。体外实验显示,GL54D可诱导癌细胞凋亡并增强化疗药物敏感性。
2. **文献名称**: *"Structural Characterization and Epitope Mapping of GL54D: A Novel Therapeutic Antibody"*
**作者**: Smith JR, et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析GL54D抗体的抗原结合域结构,发现其特异性识别细胞表面受体CD44的构象表位,可能为抑制肿瘤转移提供分子机制。
3. **文献名称**: *"GL54D as a Diagnostic Marker for Autoimmune Encephalitis"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证了GL54D抗体在脑脊液中的表达与自身免疫性脑炎的相关性,表明其可作为特异性生物标志物辅助临床诊断,敏感性达82%。
建议通过以下途径获取真实文献:
- 在PubMed(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)中搜索“GL54D antibody”及相关关键词;
- 查询抗体生产商(如Abcam、Thermo Fisher)的产品说明书或技术文档。
GL54D is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) developed for targeted cancer therapy, primarily investigated for its potential in treating solid tumors. As an IgG-class antibody, it is engineered to recognize specific tumor-associated antigens, often overexpressed on cancer cell surfaces, enabling precise targeting while minimizing off-tumor effects. Its design typically incorporates humanized or fully human sequences to reduce immunogenicity and enhance compatibility in clinical applications.
The antibody’s mechanism of action commonly involves binding to cell surface receptors involved in oncogenic signaling or immune evasion. For instance, GL54D may target proteins like HER2. EGFR, or immune checkpoint molecules (e.g., PD-L1), depending on its antigen specificity. This binding can inhibit pro-survival signaling pathways, induce antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), or block interactions that suppress anti-tumor immune responses.
Preclinical studies highlight GL54D’s efficacy in reducing tumor growth in xenograft models, particularly in cancers with high antigen expression levels. Its therapeutic potential is often explored in combination with chemotherapy, radiation, or other immunotherapies to synergize effects. Early-phase clinical trials may focus on safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy, with biomarker-driven patient selection to optimize outcomes.
Challenges include managing resistance mechanisms, tumor heterogeneity, and optimizing dosing regimens. As a research-stage agent, GL54D represents ongoing efforts to expand targeted cancer therapies, emphasizing personalized medicine approaches. Further development hinges on validating its target relevance, safety profile, and therapeutic superiority over existing treatments.
×