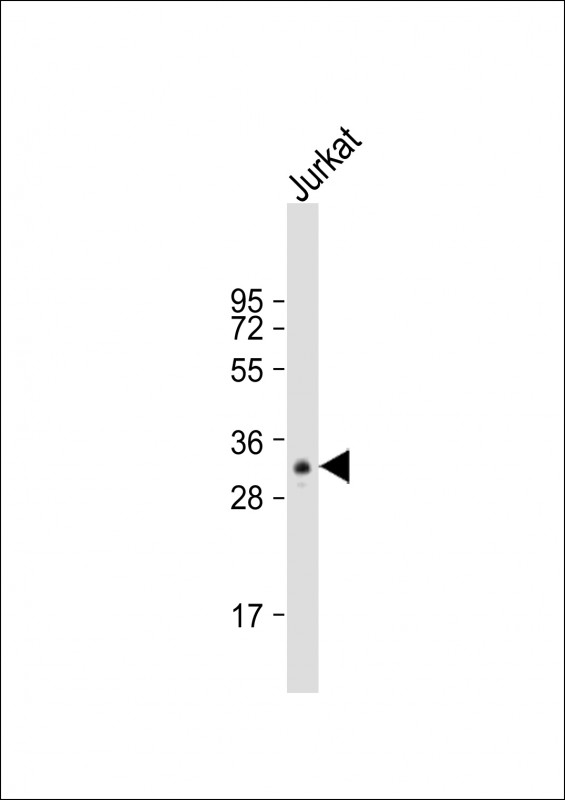

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 6 catalytic subunit, PP6C, Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 6 catalytic subunit, N-terminally processed, PPP6C, PPP6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5537 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PPP6C antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 264-293 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human PPP6C. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及PPP6C抗体的参考文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **标题**: *PPP6C regulates DNA damage response and apoptosis through modulating AMPK activity*
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用PPP6C特异性抗体验证其在DNA损伤修复中的作用,发现PPP6C通过调控AMPK信号通路影响细胞凋亡和基因组稳定性,为癌症治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
2. **标题**: *Characterization of PPP6C as a novel regulator of the NF-κB pathway in inflammatory diseases*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫沉淀和Western blot实验(使用PPP6C抗体),作者发现PPP6C通过去磷酸化TAK1负调控NF-κB通路,揭示其在炎症性疾病中的关键作用。
---
3. **标题**: *PPP6C deficiency promotes tumorigenesis via enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling*
**作者**: Chen H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过shRNA敲低PPP6C并结合抗体检测蛋白表达,证实PPP6C缺失导致β-catenin稳定性增加,促进结直肠癌进展,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的功能。
---
4. **标题**: *A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies PPP6C as a critical regulator of cell cycle progression*
**作者**: Wang R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用CRISPR筛选和PPP6C抗体验证,发现PPP6C通过调控CDK1磷酸化状态影响G2/M期转换,为细胞周期失调相关疾病提供机制解释。
---
以上文献均涉及PPP6C抗体在功能研究中的应用,涵盖癌症、炎症、细胞周期等领域。如需具体期刊信息或发表年份,可进一步补充关键词检索。
The PPP6C antibody is a crucial tool in studying the protein phosphatase 6 catalytic subunit (PPP6C), a member of the serine/threonine phosphatase family. PPP6C plays a vital role in cellular processes such as cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and immune signaling by dephosphorylating target proteins. It forms a complex with regulatory subunits (e.g., SAPS1-3. ANKRDS) to modulate substrate specificity and activity. Dysregulation of PPP6C is implicated in cancers, including melanoma and glioblastoma, where mutations or altered expression affect pathways like NF-κB or ATM/ATR signaling.
The PPP6C antibody, typically generated in rabbits or mice, enables detection and quantification of PPP6C in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Specific clones (e.g., monoclonal antibodies) target distinct epitopes, ensuring high specificity. Researchers use these antibodies to explore PPP6C's expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions in normal versus diseased tissues. Validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown is essential to confirm antibody reliability.
Applications extend to cancer research, where PPP6C antibodies help identify biomarkers or therapeutic targets. Recent studies also link PPP6C to immune regulation, emphasizing its potential in autoimmune and inflammatory disease studies. Proper optimization of antibody concentration and experimental conditions is critical to avoid cross-reactivity with related phosphatases (e.g., PP1. PP2A). Overall, PPP6C antibodies are indispensable for unraveling its biological roles and clinical relevance.
×