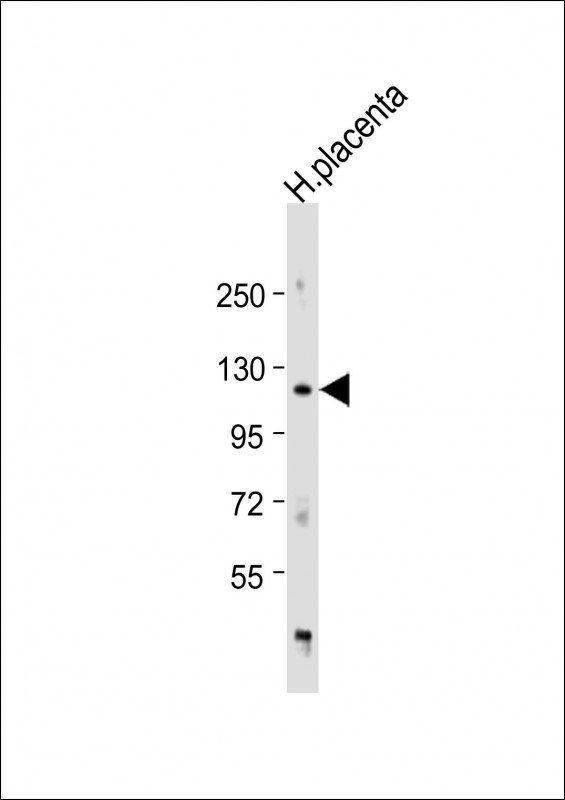
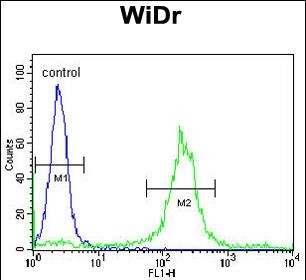
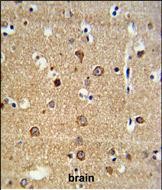
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 19, ADAM 19, 3424-, Meltrin-beta, Metalloprotease and disintegrin dendritic antigen marker, MADDAM, ADAM19, MLTNB |
| Entrez GeneID | 8728 |
| WB Predicted band size | 105.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ADAM19 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 207-236 amino acids from the Central region of human ADAM19. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于ADAM19抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要概括内容:
1. **文献名称**:*ADAM19 is essential for cardiac morphogenesis and function during mouse development*
**作者**:Zhou HM, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ADAM19基因敲除小鼠及特异性抗体,发现ADAM19在小鼠心脏发育中通过调控神经调节蛋白信号通路影响心内膜垫形成和心室结构,抗体染色显示其在内皮细胞中高表达。
2. **文献名称**:*ADAM19 expression in human cancers: A potential marker for tumor progression*
**作者**:Kodama T, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析ADAM19抗体在多种癌症组织中的表达,发现其在乳腺癌、肺癌中显著上调,与肿瘤侵袭性及患者预后不良相关,提示ADAM19可能作为癌症治疗的靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*ADAM19 regulates TGF-β signaling pathway through cleavage of fibrillin-1*
**作者**:Li Q, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用ADAM19抗体进行Western blot和免疫共沉淀实验,证明ADAM19通过切割细胞外基质蛋白fibrillin-1调控TGF-β信号通路,影响成纤维细胞分化及纤维化疾病进程。
注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“ADAM19 antibody”获取。
ADAM19 (A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 19) is a member of the ADAM family of transmembrane proteins, which are characterized by their dual roles in cell adhesion and proteolytic processing. Initially identified in the early 2000s, ADAM19 is encoded by the ADAM19 gene and is expressed in various tissues, including the nervous system, cardiovascular system, and skeletal structures. Structurally, it contains a prodomain, metalloproteinase domain, disintegrin-like domain, transmembrane region, and cytoplasmic tail, enabling interactions with extracellular matrix components and cell surface receptors.
Functionally, ADAM19 is implicated in ectodomain shedding of growth factors, cytokines, and adhesion molecules, regulating signaling pathways critical for development and tissue homeostasis. Studies highlight its role in embryogenesis, particularly in heart valve formation, neural crest cell migration, and bone development. Dysregulation of ADAM19 has been associated with pathological conditions such as cancer, fibrosis, and inflammatory diseases. In cancer, it may promote tumor progression by modulating cell adhesion, invasion, and angiogenesis.
Antibodies targeting ADAM19 are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and mechanistic roles. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to study protein levels in disease models or developmental contexts. Some research explores ADAM19 antibodies for therapeutic potential, aiming to inhibit its proteolytic activity in pathological states. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity and understanding isoform variations. Ongoing studies continue to unravel its complex biology, positioning ADAM19 as a promising target for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
×