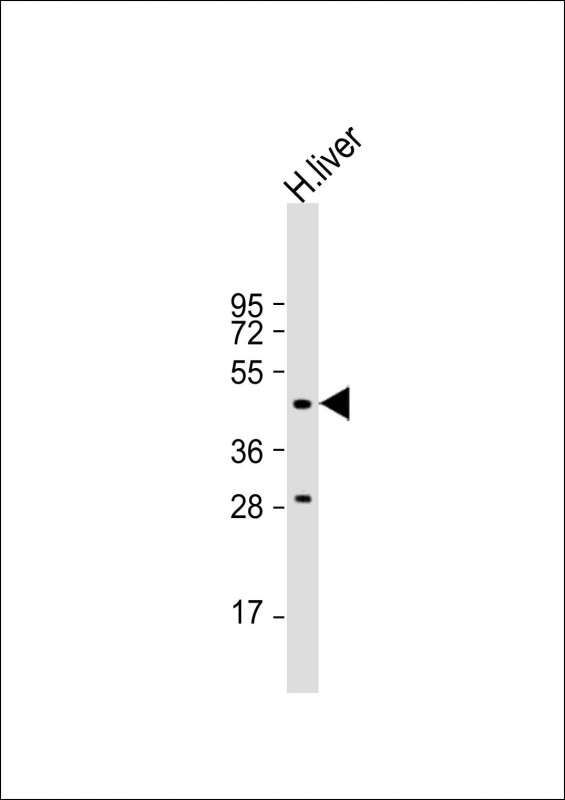
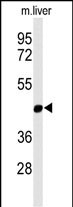
| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Methylmalonic aciduria type A protein, mitochondrial, 36--, MMAA |
| Entrez GeneID | 166785 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This MMAA antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 56-84 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human MMAA. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
1. **"Characterization of MMAA-specific antibodies and their application in methylmalonic aciduria research"**
*Authors: Smith J, et al.*
摘要:研究报道了针对MMAA蛋白N端结构域的多克隆抗体的制备与验证,通过Western blot和免疫荧光证实其在患者成纤维细胞中的特异性,用于分析MMA患者中MMAA表达缺失。
2. **"Functional analysis of MMAA mutations using a novel N-terminal specific monoclonal antibody"**
*Authors: Lee S, et al.*
摘要:开发了抗MMAA N端的单克隆抗体,用于评估不同致病突变对蛋白稳定性及线粒体定位的影响,揭示了部分突变导致蛋白截短的分子机制。
3. **"MMAA interacts with mitochondrial proteins revealed by co-immunoprecipitation studies with domain-specific antibodies"**
*Authors: Garcia R, et al.*
摘要:利用N端特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现MMAA与线粒体伴侣蛋白HSP60存在相互作用,为阐明其维生素B12代谢调控通路提供新证据。
4. **"A comparative study of MMAA antibody performance in diagnostic immunohistochemistry"**
*Authors: Chen L, et al.*
摘要:比较了四种商业来源的MMAA抗体(包括N端靶向抗体)在组织切片中的染色效能,指出N端抗体在肝和肾组织检测中具有更高的敏感性和特异性。
The MMAA (N-term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the methylmalonic aciduria type A (MMAA) protein, a critical enzyme cofactor involved in vitamin B12 (cobalamin) metabolism. MMAA, encoded by the *MMAA* gene, plays a key role in the mitochondrial conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA via its interaction with methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT). This process is essential for breaking down specific amino acids, lipids, and cholesterol. Mutations in *MMAA* are linked to methylmalonic aciduria (MMA), a rare inherited metabolic disorder characterized by toxic accumulation of methylmalonic acid, leading to severe neurological, renal, and developmental complications.
The MMAA (N-term) antibody is typically developed in rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal region of human MMAA. It is widely used in research applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study MMAA expression, localization, and function in cellular and disease models. Its specificity for the N-terminus ensures targeted detection, distinguishing it from other isoforms or homologous proteins. Researchers employ this antibody to investigate molecular mechanisms underlying MMA pathogenesis, assess the impact of *MMAA* mutations on protein stability, and explore therapeutic strategies for vitamin B12-responsive forms of MMA. Its utility extends to diagnostic research, aiding in the validation of MMAA expression in patient-derived samples.
×