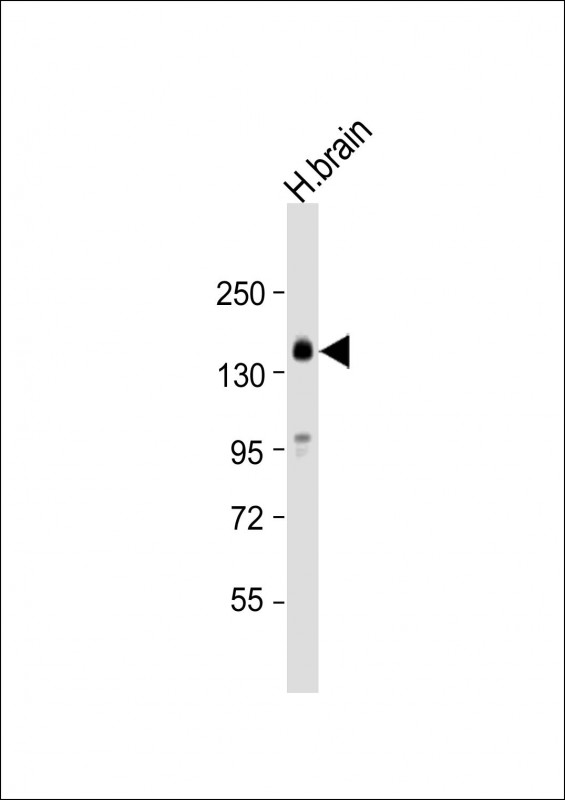

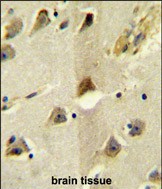
| WB | 1/1000-1/4000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Solute carrier family 12 member 5, Electroneutral potassium-chloride cotransporter 2, K-Cl cotransporter 2, hKCC2, Neuronal K-Cl cotransporter, SLC12A5, KCC2, KIAA1176 |
| Entrez GeneID | 57468 |
| WB Predicted band size | 126.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SLC12A5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 5-33 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SLC12A5. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SLC12A5(KCC2)N端抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
---
1. **"Developing networks play a melody of plasticity via KCC2"**
*作者:Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA, Kaila K*
*摘要*:该研究探讨了KCC2在神经元发育中的表达变化及其对抑制性神经传递的作用,通过N端特异性抗体验证了KCC2在早期突触可塑性中的关键功能。
2. **"A novel role for MAPKAPK2 in the regulation of KCC2 phosphorylation and chloride homeostasis"**
*作者:Lee HHC, Deeb TZ, Walker JA, et al.*
*摘要*:文章利用针对KCC2 N端的抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,揭示了MAPKAPK2介导的磷酸化对KCC2氯离子转运活性的调控机制。
3. **"KCC2 interacts with the dendritic cytoskeleton to promote spine development"**
*作者:Gauvain G, Chamma I, Chevy Q, et al.*
*摘要*:研究通过N端特异性抗体结合免疫荧光技术,证实KCC2通过与细胞骨架蛋白相互作用,调控树突棘的形成和突触功能的成熟。
---
这些文献均涉及使用或验证针对SLC12A5(KCC2)N端的抗体,涵盖其在离子稳态、信号转导及神经元形态学中的作用研究。
The SLC12A5 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the solute carrier family 12 member 5 (SLC12A5) protein, also known as the potassium-chloride cotransporter 2 (KCC2). Encoded by the SLC12A5 gene, KCC2 is a neuron-specific transporter critical for maintaining chloride ion homeostasis in the central nervous system. It facilitates the electroneutral efflux of potassium and chloride ions, which is essential for establishing the reversal potential of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mediated neurotransmission. Dysregulation of KCC2 has been implicated in neurological disorders, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and autism spectrum disorders.
The N-terminal antibody specifically recognizes epitopes within the cytoplasmic N-terminal domain of KCC2. enabling researchers to study its expression, localization, and post-translational modifications. This region is vital for transporter regulation, as it contains phosphorylation sites and interaction domains that modulate KCC2 activity. The antibody is widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate KCC2's role in neuronal development, synaptic plasticity, and disease mechanisms. Its specificity for the N-terminus helps differentiate KCC2 from other SLC12 family members, though cross-reactivity with splice variants or homologous proteins should be validated experimentally. Overall, this tool is indispensable for exploring KCC2-related pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets.
×