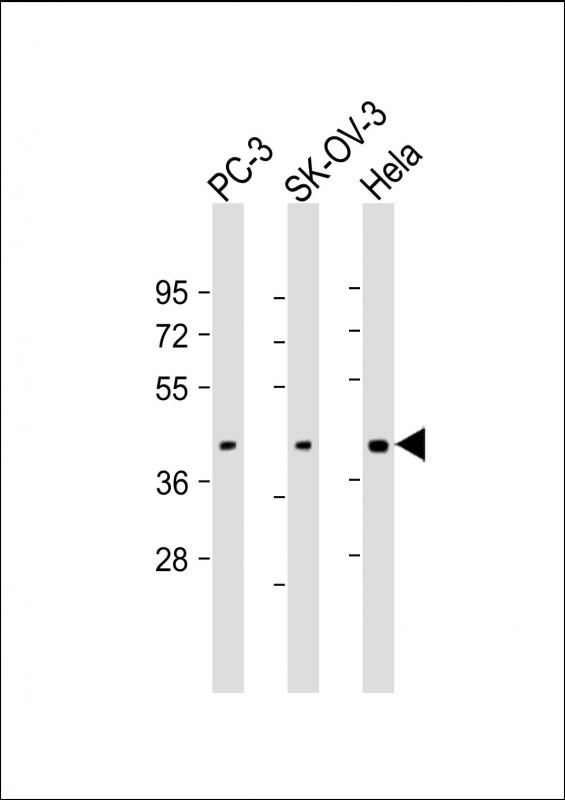
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CMP-N-acetylneuraminate-beta-galactosamide-alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 4, Alpha 2,3-ST 4, Beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 4, 2.4.99.-, Alpha 2,3-sialyltransferase IV, Gal-NAc6S, Gal-beta-1,4-GalNAc-alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase, SAT-3, ST-4, ST3Gal IV, ST3GalIV, ST3GalA.2, STZ, Sialyltransferase 4C, SIAT4-C, ST3GAL4, CGS23, NANTA3, SIAT4C, STZ |
| Entrez GeneID | 6484 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ST3GAL4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 26-57 amino acids from human ST3GAL4. |
+ +
以下是关于ST3GAL4 (N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*ST3GAL4-mediated sialylation regulates breast cancer metastasis via CD44-EGFR signaling*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了ST3GAL4在乳腺癌中通过N端结构域调控CD44的唾液酸化修饰,增强EGFR信号通路,促进肿瘤转移。实验中利用ST3GAL4 (N-Term)抗体进行免疫沉淀和免疫荧光,证实其与CD44的相互作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Role of ST3GAL4 in T-cell activation and autoimmune disease progression*
**作者**:Li H, et al.
**摘要**:通过ST3GAL4 (N-Term)抗体的阻断实验,发现ST3GAL4在T细胞表面糖基化中起关键作用,影响T细胞受体(TCR)信号转导,并促进自身免疫性疾病的发展。研究强调了该抗体在功能研究中的特异性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a novel ST3GAL4 monoclonal antibody for glioblastoma diagnostics*
**作者**:Wang Q, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种针对ST3GAL4 N端表位的新型单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在胶质母细胞瘤组织中的高特异性和敏感性,证实其可用于临床病理诊断及预后评估。
---
如需更多文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“ST3GAL4 antibody N-terminal”为关键词进一步检索。
The ST3GAL4 (N-Term) antibody is a tool designed to detect the N-terminal region of the ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2.3-sialyltransferase 4 (ST3GAL4), a key enzyme in glycosylation processes. ST3GAL4 belongs to the sialyltransferase family, which catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid to terminal galactose residues on glycoproteins and glycolipids, forming α-2.3 linkages. This post-translational modification influences cell-cell interactions, immune responses, and receptor signaling. Dysregulation of ST3GAL4 has been implicated in cancer metastasis, inflammation, and neurodegenerative disorders, making it a research focus in disease mechanisms.
Structurally, ST3GAL4 is a type II transmembrane protein with a short N-terminal cytoplasmic tail, a transmembrane domain, and a catalytic domain in the Golgi lumen. The N-Term antibody specifically targets epitopes near the protein’s cytoplasmic region, enabling studies of its expression, localization, and regulation. It is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess ST3GAL4 levels in cell lysates or tissues. Validated in multiple species, this antibody aids in exploring ST3GAL4’s role in modulating cell surface sialylation patterns and its association with pathological states. Researchers rely on its specificity to dissect glycosylation-related pathways in developmental biology, immunology, and oncology.
×