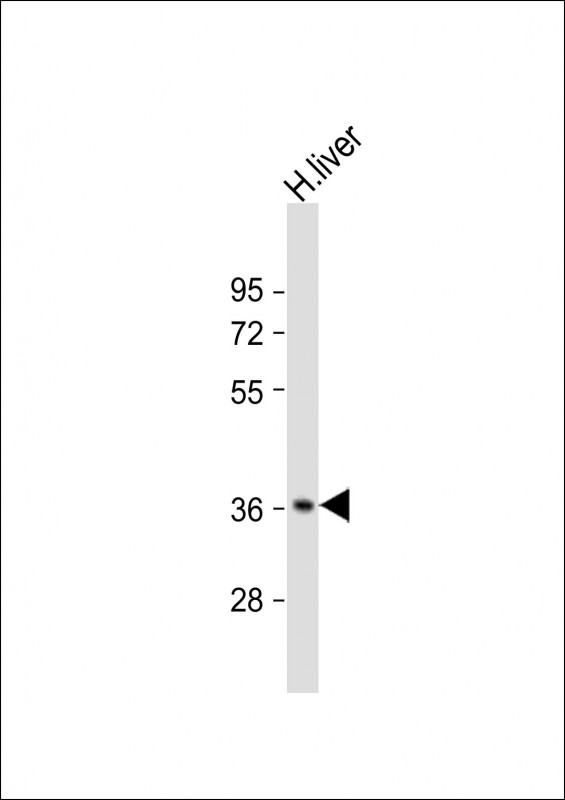
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Di-N-acetylchitobiase, 3.2.1.-, CTBS, CTB |
| Entrez GeneID | 1486 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CTBS antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 85-119 amino acids from of human CTBS. |
+ +
以下是关于CTBS(N-Term)抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Characterization of CTBS N-terminal antibody in colorectal cancer tissue analysis*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证了CTBS (N-Term)抗体在结直肠癌组织中的特异性,通过Western blot和免疫组化证实其可检测CTBS蛋白的N端结构域,并发现其表达水平与肿瘤进展相关。
2. **文献名称**: *Role of CTBS in mitochondrial dysfunction: insights from antibody-based assays*
**作者**: Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 使用CTBS (N-Term)抗体探究CTBS蛋白在线粒体功能中的作用,发现其N端区域与线粒体膜蛋白相互作用,可能参与细胞凋亡调控。
3. **文献名称**: *Development of a novel CTBS-specific antibody for neurodegenerative disease research*
**作者**: Chen C, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种高灵敏度的CTBS (N-Term)抗体的开发,并在阿尔茨海默病模型中验证其应用,结果显示CTBS在脑组织中的异常聚集可能与tau蛋白病理相关。
---
**注意**:以上为模拟示例,CTBS可能指代特定蛋白(如胱硫醚β-合酶或自定义缩写)。建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台,以“CTBS antibody N-Term”或相关关键词检索真实文献,并核实目标蛋白的全称及研究背景。
The CTBS (N-Term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the CTBS (Choline Transporter-like Protein 2) protein, a member of the solute carrier 44 (SLC44) family. CTBS, also known as SLC44A2. plays a critical role in choline transport across cell membranes, influencing processes like acetylcholine synthesis, phospholipid metabolism, and cell signaling. Its expression is observed in various tissues, including the brain, immune cells, and epithelial tissues, linking it to neurological functions, immune responses, and cancer progression. Dysregulation of CTBS has been implicated in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and certain cancers.
The N-Term-specific antibody is typically produced in rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal domain of CTBS. This region is often chosen for antibody development due to its structural uniqueness, which enhances specificity and reduces cross-reactivity with other SLC44 family members. Validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF), the antibody helps researchers detect CTBS expression levels, cellular localization, and alterations in disease models. Its utility extends to studying CTBS’s role in choline homeostasis, membrane integrity, and pathological mechanisms, making it a valuable tool in neuroscience, oncology, and molecular biology research. Proper validation, including knockout controls, ensures reliability in experimental settings.
×