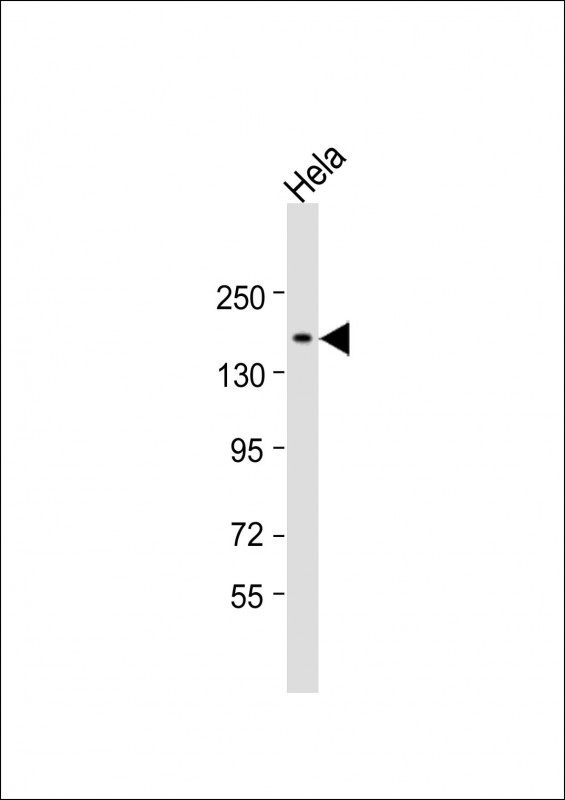
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 5, CHD-5, 3.6.4.12, ATP-dependent helicase CHD5, CHD5 {ECO:0000312|EMBL:AAL98962.1}, KIAA0444 |
| Entrez GeneID | 26038 |
| WB Predicted band size | 223.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CHD5 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 64-98 amino acids from human CHD5. |
+ +
以下是关于 **CHD5 (N-Term)** 抗体的3篇参考文献,简要概括了文献内容:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CHD5 is a tumor suppressor at human 1p36*
**作者**:Bagchi A. et al.
**摘要**:研究证实CHD5作为1p36区域的肿瘤抑制因子,通过免疫沉淀和Western blot(使用N端特异性抗体)发现其与神经母细胞瘤发生相关,并参与染色质重塑复合物调控。
2. **文献名称**:*The chromatin remodeler CHD5 restricts glioblastoma through p53-independent apoptosis*
**作者**:Paul S. et al.
**摘要**:利用CHD5 N-Term抗体进行免疫组化分析,揭示CHD5在胶质母细胞瘤中通过非p53依赖性凋亡通路抑制肿瘤进展,且低表达与患者不良预后相关。
3. **文献名称**:*CHD5 deficiency promotes intestinal inflammation and carcinogenesis*
**作者**:Wang X. et al.
**摘要**:通过N-Term抗体检测CHD5在结直肠癌中的表达,发现CHD5缺失通过调控炎症信号通路(如NF-κB)促进肠道炎症和癌变。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“CHD5 antibody N-Term”检索最新研究,并确认抗体验证细节(如品牌、克隆号等)。
The CHD5 (N-Term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the Chromodomain Helicase DNA-Binding Protein 5 (CHD5), a member of the CHD family of chromatin remodelers. CHD5 is a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 1p36.3. a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other cancers. It plays a critical role in chromatin remodeling, gene regulation, and maintaining genomic stability by facilitating the formation of repressive chromatin states. CHD5 is highly expressed in the nervous system and is essential for neural development, differentiation, and neuronal function. Its loss or mutation is associated with aggressive cancers, poor prognosis, and impaired DNA damage response.
The N-terminal region of CHD5 contains conserved domains involved in protein-protein interactions and chromatin binding, making it a key functional domain. Antibodies targeting this region are widely used in research to study CHD5 expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interactions with chromatin or other regulatory proteins. They are valuable tools in applications such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Studies using CHD5 (N-Term) antibodies have contributed to understanding its role in tumor suppression, neural development, and epigenetic regulation, as well as its potential as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis or therapeutic targeting. Validation of specificity, including knockout controls, is critical due to homology shared among CHD family members.
×