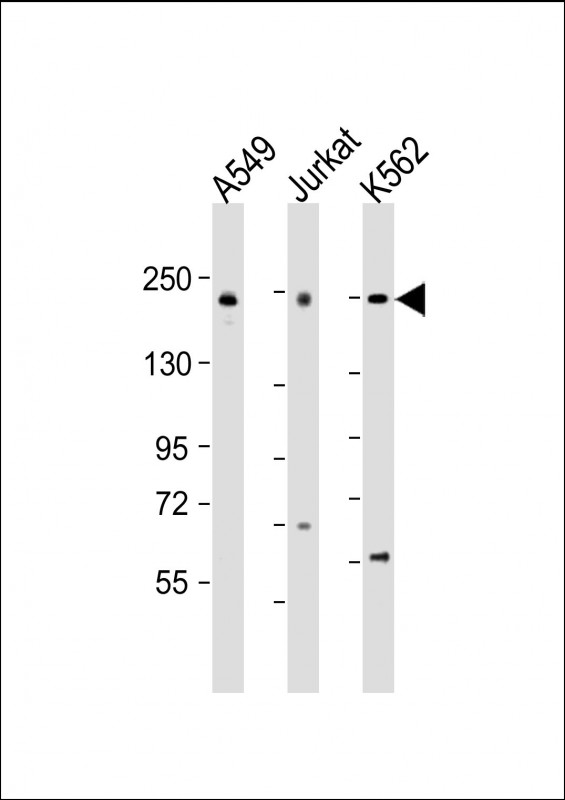
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Proteasome activator complex subunit 4, Proteasome activator PA200, PSME4, KIAA0077 |
| Entrez GeneID | 23198 |
| WB Predicted band size | 211.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This PSME4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 503-535 amino acids from human PSME4. |
+ +
以下是关于PSME4 (N-Term)抗体的3篇文献摘要简述:
1. **文献名称**:*Characterization of PSME4 as a novel immunoproteasome regulator in cancer cells*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种靶向PSME4 N端结构域的特异性抗体,用于检测其在肿瘤细胞中的表达。结果显示PSME4通过调控免疫蛋白酶体活性促进肿瘤免疫逃逸,Western blot和免疫荧光实验验证了抗体的特异性。
2. **文献名称**:*PSME4 interacts with the 20S proteasome and modulates its activity in neurodegenerative models*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种针对PSME4 N端的单克隆抗体,证实其在小鼠脑组织中的结合能力。实验表明PSME4与20S蛋白酶体结合并影响其活性,可能与阿尔茨海默病中蛋白聚集相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a PSME4-specific antibody for functional studies in autoimmune disorders*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:文章描述了PSME4 (N-Term)抗体的制备及验证(包括ELISA和免疫组化)。研究发现PSME4在类风湿关节炎患者的巨噬细胞中高表达,可能通过调节炎症信号通路发挥作用。
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如“PSME4 antibody N-terminal”)获取。建议结合具体研究领域筛选近年发表的论文。
The PSME4 (N-Term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the Proteasome Activator Subunit 4 (PSME4), a protein also known as PA200. PSME4 is a member of the PA28/PSME family of proteasome regulators, which modulate the activity of the 20S proteasome, a multi-subunit complex responsible for degrading ubiquitinated proteins. Unlike other PA28 family members (e.g., PSME1-3), PSME4 contains a unique HEAT-repeat domain at its N-terminus, which facilitates interactions with the proteasome and promotes the degradation of specific substrates, including histone complexes and damaged proteins. PSME4 is primarily localized in the nucleus and is implicated in DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and cellular stress responses. Studies suggest its role in maintaining genomic stability and regulating cell cycle progression.
The PSME4 (N-Term) antibody is widely used in research to investigate PSME4 expression, localization, and function. It is validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. This antibody is particularly valuable in studies exploring proteasome dynamics in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging, as dysregulation of PSME4 has been linked to tumor progression (e.g., glioblastoma, breast cancer) and impaired protein homeostasis. By detecting the N-terminal epitope, the antibody helps distinguish PSME4 from other proteasome activators, aiding mechanistic studies of its unique regulatory roles. Recent research also highlights its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target in diseases associated with proteasomal dysfunction.
×