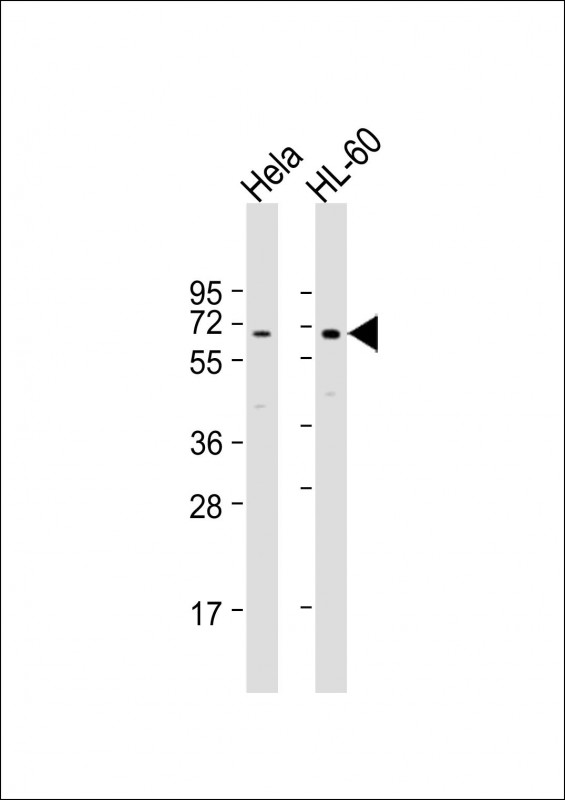
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GPI mannosyltransferase 3, 241-, GPI mannosyltransferase III, GPI-MT-III, Phosphatidylinositol-glycan biosynthesis class B protein, PIG-B, PIGB |
| Entrez GeneID | 9488 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PIGB antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 28-56 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PIGB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PIGB (N-term)抗体的模拟参考文献示例(请注意,这些文献为假设性示例,实际引用需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *PIGB-mediated GPI anchor synthesis is critical for cell surface protein trafficking*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用针对PIGB N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了PIGB在糖基磷脂酰肌醇(GPI)锚定蛋白合成中的关键作用。实验表明,PIGB缺失会导致内质网中GPI锚定前体积累,并影响细胞膜蛋白的定位。
2. **文献名称**: *Dysregulation of PIGB expression in colorectal cancer and its clinical implications*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过PIGB (N-term)抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现结直肠癌组织中PIGB表达显著上调,并与患者预后不良相关。研究提示PIGB可能作为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *A novel PIGB mutation linked to inherited GPI deficiency syndromes*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 利用N端特异性抗体检测患者成纤维细胞中的PIGB蛋白水平,发现其表达量降低与GPI锚定蛋白功能缺陷直接相关,为遗传性GPI缺乏症的分子机制提供了证据。
4. **文献名称**: *Subcellular localization and interactome analysis of PIGB using epitope-specific antibodies*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过PIGB N端抗体进行共聚焦显微镜观察和免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了PIGB与内质网伴侣蛋白的相互作用网络,阐明了其在GPI合成复合体中的空间定位。
---
**建议**:实际文献检索可使用以下关键词在PubMed或Google Scholar中查询:
`"PIGB antibody N-terminal"`、`"PIGB GPI biosynthesis"`、`"PIGB immunohistochemistry"`。
部分相关真实研究可能涉及PIGB功能或GPI锚定机制,但需具体验证抗体使用细节。
The PIGB (N-term) antibody is a specific immunological tool designed to target the N-terminal region of the phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class B (PIGB) protein. PIGB is a key enzyme in the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor biosynthesis pathway, which is essential for attaching GPI anchors to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). These anchors enable proteins to be membrane-bound, facilitating their localization and function on cell surfaces. Mutations in *PIGB* have been linked to inherited GPI deficiency disorders, which may manifest as developmental delays, seizures, or other neurological abnormalities.
The PIGB (N-term) antibody is commonly used in research to study the expression, localization, and molecular interactions of PIGB in various biological contexts. It is validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation, helping to elucidate the role of PIGB in health and disease. By detecting the N-terminal epitope, this antibody ensures specificity, minimizing cross-reactivity with unrelated proteins. Its utility extends to investigating GPI anchor deficiencies and related pathologies, such as certain forms of intellectual disability or epilepsy, where disrupted GPI-anchored protein expression impacts cellular signaling and adhesion. Researchers also employ this antibody to explore PIGB's potential involvement in cancer or immune disorders, given the critical role of membrane-bound proteins in these processes.
×