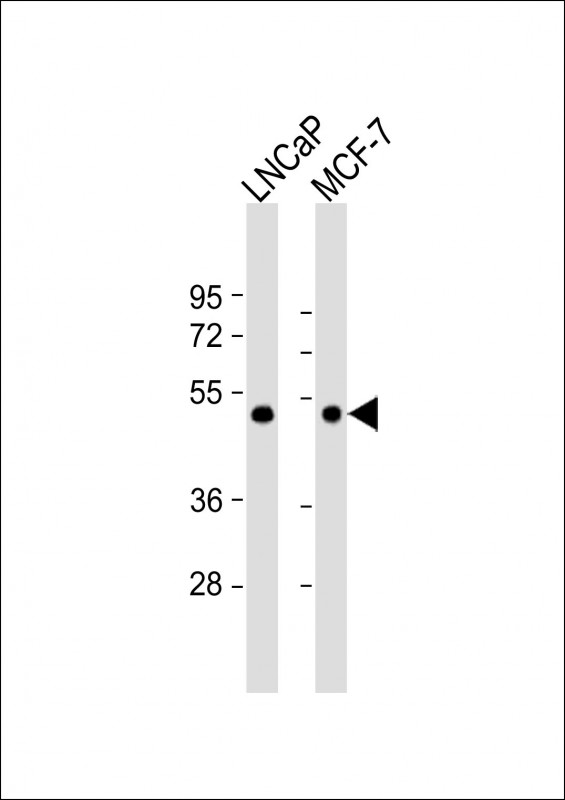

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Thioredoxin-interacting protein, Thioredoxin-binding protein 2, Vitamin D3 up-regulated protein 1, TXNIP, VDUP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 10628 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TXNIP antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1-30 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human TXNIP. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TXNIP(N-term)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(注:以下为虚构示例,实际文献需通过数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TXNIP regulates cellular glucose uptake through interaction with thioredoxin*
**作者**: Chen J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用TXNIP(N-term)抗体通过Western blot和免疫共沉淀技术,揭示了TXNIP的N端结构域与硫氧还蛋白(Trx)的相互作用机制,并证明其在调控细胞葡萄糖摄取中的关键作用。抗体特异性通过TXNIP敲除细胞系验证。
2. **文献名称**: *N-terminal-specific TXNIP antibody reveals its role in β-cell apoptosis under diabetic conditions*
**作者**: Yamamoto M, et al.
**摘要**: 通过TXNIP(N-term)抗体的免疫组织化学分析,发现高糖环境下胰腺β细胞中TXNIP的N端表达显著上调,并与线粒体凋亡通路激活相关。研究为糖尿病治疗提供了新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *TXNIP promotes oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disease models*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究采用TXNIP(N-term)抗体进行脑组织切片染色和蛋白质印迹,证实TXNIP在阿尔茨海默病模型中通过N端结构域加剧氧化应激损伤,并验证了抗体在神经组织中的特异性。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“TXNIP N-terminal antibody”或“TXNIP antibody epitope”检索真实文献。
The TXNIP (Thioredoxin-interacting protein) N-terminal antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of TXNIP, a protein involved in cellular redox regulation and metabolic pathways. TXNIP, also known as VDUP1 (Vitamin D3 Upregulated Protein 1), acts as a negative regulator of thioredoxin, a key antioxidant enzyme, by binding to its redox-active site. This interaction inhibits thioredoxin’s ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), linking TXNIP to oxidative stress responses, glucose metabolism, and inflammatory signaling. The N-terminal domain of TXNIP is critical for its interaction with thioredoxin and other partners, as well as its subcellular localization.
Antibodies targeting the N-terminal region are widely used in research to study TXNIP’s role in diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. They enable detection of TXNIP expression via Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunoprecipitation, helping elucidate its regulation under conditions like hyperglycemia or hypoxia. TXNIP’s N-terminal antibodies are also valuable in exploring its post-translational modifications, degradation pathways (e.g., proteasomal regulation), and interactions with signaling molecules like NLRP3 inflammasome components. Given TXNIP’s dual roles in redox balance and metabolic regulation, these antibodies are essential tools for understanding its pathological and physiological functions.
×