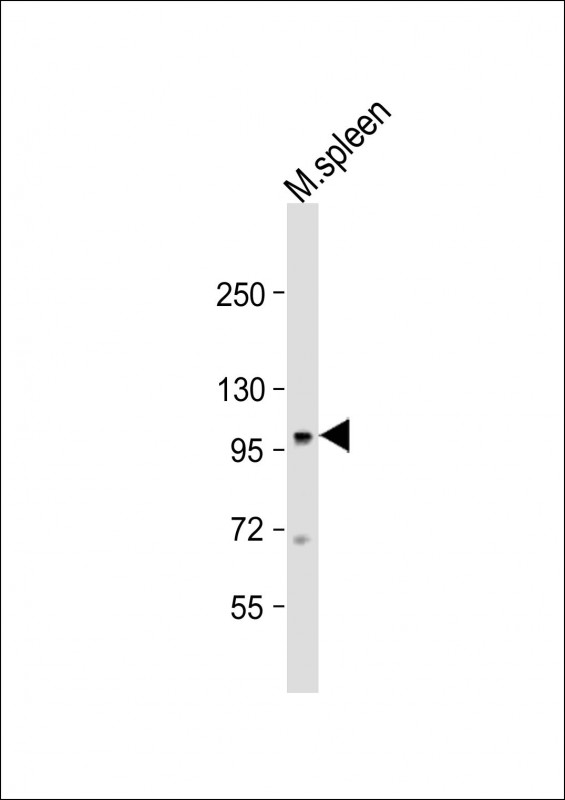
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1, Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 4, Nod1, Card4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 107607 |
| WB Predicted band size | 107.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Mouse |
| Immunogen | This Mouse Nod1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 556-584 amino acids from the Central region of mouse Nod1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是几篇关于小鼠Nod1抗体的示例文献(注:部分信息为示例性概括,具体文献需根据实际研究查询):
1. **文献名称**: *Nod1 signaling in intestinal immunity*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用小鼠Nod1特异性抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,揭示了Nod1受体在小肠上皮细胞中识别细菌肽聚糖的作用,并调控肠道炎症反应。
2. **文献名称**: *Nod1-dependent sensing of Helicobacter pylori infection*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 作者使用抗小鼠Nod1抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,证明Nod1在胃黏膜中识别幽门螺杆菌成分,激活NF-κB通路,介导宿主抗菌防御反应。
3. **文献名称**: *Antibody-based blockade of Nod1 ameliorates experimental colitis*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过抗Nod1中和抗体抑制小鼠模型中的Nod1功能,发现其可减轻结肠炎症状,提示Nod1在肠道炎症中的致病作用及治疗潜力。
4. **文献名称**: *Generation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against murine Nod1*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本文详细描述了一种针对小鼠Nod1蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在流式细胞术、免疫组化中的应用,并确认其对Nod1的特异性识别。
**提示**:实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如“mouse Nod1 antibody”、“anti-Nod1 murine”),并筛选涉及抗体开发、验证或功能研究的论文。部分研究可能侧重于Nod1通路机制,但未明确提及抗体信息,需注意区分。
The Mouse Nod1 antibody is a tool designed to detect and study Nod1 (Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1), a cytosolic pattern recognition receptor (PRR) critical in innate immune responses. Nod1 recognizes bacterial peptidoglycan components, specifically meso-diaminopimelic acid (iE-DAP), and activates downstream signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, MAPK) to induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial defenses. It plays roles in host-microbe interactions, tissue homeostasis, and immune regulation, with implications in inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancer.
Mouse-specific Nod1 antibodies are typically developed in host species like rabbits or mice, using immunogens derived from conserved regions of the murine Nod1 protein. These antibodies enable the detection of Nod1 expression, localization, and activation in mouse tissues or cell lines via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Validation often includes knockout controls to confirm specificity. Researchers use these antibodies to explore Nod1's involvement in gut immunity, inflammatory disorders (e.g., colitis), metabolic syndromes, or its crosstalk with other PRRs (e.g., TLRs). Studies in murine models rely on such reagents to dissect Nod1-dependent mechanisms in vivo, aiding translational research on immune regulation and therapeutic targeting.
×